Arteries, veins and capillaries – they are the blood vessels of the body’s intricate plumbing system. They run throughout our body; the bursting of one of them in the brain can have serious detrimental effects, known as a haemorrhagic stroke. An immediate consequence of this condition is bleeding on the brain. Below we are going to look into this in detail.
What Does Bleeding inside the Brain Mean (Bleeding in Brain)?
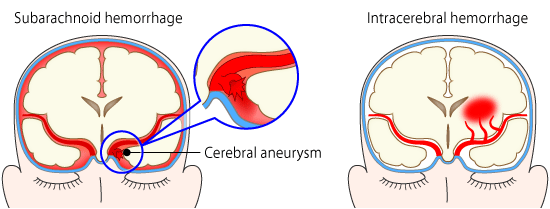
Bleeding on the brain or haemorrhage can occur in two ways, blood vessels can rupture inside the brain (intracerebral haemorrhage) or on the surface (subarachnoid haemorrhage).
1. Intracerebral Haemorrhage
One in ten strokes is caused due to the rupture of an artery within the brain. Blood bursts out at high pressure from the artery and can cause serious damage as it impacts the brain tissue. It can result in body feeling weak, numbing of one side of the body, unclear vision, trouble communicating with other people, etc.
2. Subarachnoid Haemorrhage
A series of membranes protect the brain from damage and the space between two layers of them is the subarachnoid space which is filled with cerebrospinal fluid. Damage to blood vessels on the brain’s surface can cause blood to leak into this space, resulting in a stroke. This is a very serious condition and takes up about 5% of all stroke cases. The most immediate impact of this kind of haemorrhage is intense pain and altered consciousness.
What Causes Bleeding on the Brain (Bleeding in Brain)?
There can be a number of causes for brain haemorrhage; here are a few of the common ones:
1. High Blood Pressure
Hypertension or high blood pressure can make the arteries weak and over time cause them to rupture. This accounts for over 60% of haemorrhages and there are a number of risk factors that make a person more likely to suffer from hypertension, such as limited exercise, excess body weight, increased consumption of alcohol, cigarettes and a lot of stress.
2. Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy
This condition is more likely with advanced age and is caused due to the accumulation of a protein called amyloid in the blood vessels. As the quantity of amyloid increases, the artery will tear and cause bleeding on the brain. This usually occurs near the surface of the brain and in 63% of the cases the blood leaks into the subarachnoid space.
3. Aneurysm
The walls of arteries in the brain are generally thick and this helps withstand small periods of high blood pressure. However, some parts of these arteries can become weak and bulge out. These bulges on arteries are called aneurysms and can occur at birth or during the course of one’s life. An increase in blood pressure can cause an aneurysm to burst at any time, causing a brain haemorrhage.
4. Abnormal Blood Vessels
Rare congenital abnormalities in blood vessels can make the blood vessels tangled or oversized. They usually have weak walls and changes in blood pressure can cause them to rupture. Some examples of this condition are arteriovenous malformation, cavernous malformation and developmental venous anomaly.
5. Medication
Drugs known as anticoagulants help prevent blood clots in people at risk of suffering from a stroke. However the incorrect use of this medicine can cause bleeding on the brain.
6. Illegal Drugs
Some illicit drugs like cocaine can cause the walls of blood vessels to weaken. This will increase the chances of blood vessel rupture and haemorrhage.
How to Treat This Condition
Bleeding in brain is a life-threatening issue but early detection and the advances of modern medicine help many patients overcome its numerous dangers. Here are some of the main treatments:
1. Control Blood Pressure
As mentioned above, over 60% of haemorrhages occur due to hypertension but this can be controlled with deliberate efforts. In the event of a blood vessel rupture, doctors administer intravenous medicines to lower the blood pressure and decrease the outflow. Patients are generally provided sedatives to prevent exertion of the body.
2. Repair a Ruptured Blood Vessel
In some cases, the damage can be controlled through surgery. An experienced surgeon can clip the ends of an aneurysm to block the flow of blood. This will stop the bleeding on the brain effectively. However, this process is risky and can have serious repercussions. The decision for a surgery is made after taking into account the patient’s age, health and the particulars of the ruptured blood vessel.
3. Remove the Blood Clots
Bleeding on the brain can lead to the pooling of blood in one location. This forms a big clot and is called a hematoma. The hematoma takes up extra space in the skull and exerts undue pressure on the brain tissue. This can lead to serious damage to the brain and in most cases surgery is performed to remove it. However, the process contains inherent risks, so surgery is avoided when the clot is located near fragile brain stem components.
4. Prevent Cerebrospinal Fluid Blockage
Bleeding on the brain can interrupt the flow of cerebrospinal fluid. This fluid is circulated through the brain to provide necessary nutrition and carry away cellular waste; its blockage can cause serious damage to the brain as the fluid is unable to leave the skull. Surgeons may opt to provide an extra-ventricular drain (EVD) for its smooth drainage from the brain. The EVD provides a direct connection from the cerebral cavity to the outside of the body. Hence it has to be kept clean at all times. This is a temporary fixture but a permanent drainage fixture, called a shunt, can be installed if required.
