Addison's disease is something that can strike anyone at any age and affects the person's adrenal glands. This disease, which is often referred to as hypocortisolism or chronic adrenal insufficiency, happens when a person's adrenal glands are not able to product enough hormones. What happens is that there is an insufficient amount of cortisol and sometimes aldosterone. Addison's disease can prove to be life threatening.
Addison's Disease Symptoms
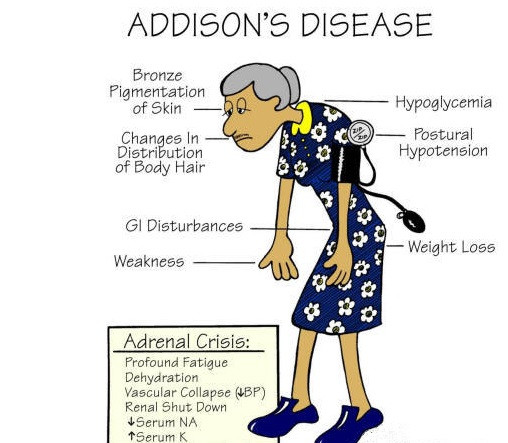
Addison's disease can affect people in different ways when it comes to symptoms. The individual may suffer from just one or a whole host of different symptoms. It's also important to note that these symptoms don't usually just suddenly appear; instead, they build slowly over time. Here's a look at some of the most common symptoms that go hand-in-hand with the disease.
- Depression
- A craving for salty foods and salt
- A decrease in the appetite, weight loss
- Diarrhea, nausea, and/or vomiting
- General fatigue and muscle weakness
- Low blood pressure that can result in the person fainting
- Hyperpigmentation (skin that gets darker)
- Irritability
- Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar)
- Joint and muscle pains
- Loss of body hair
- Sexual dysfunction (in women)
Addisonian Crisis Symptoms
- Now if the person is suffering from acute adrenal failure, which is called an Addisonian crisis, the symptoms are quick to appear. These symptoms can include:
- Low blood pressure
- Hyperkalemia (high potassium levels)
- A loss of consciousness
- Pain in the legs, abdomen, and/or lower back
- Severe cases of diarrhea and vomiting, this can result in dehydration
When to See a Doctor
It's important to visit the doctor if you develop or suddenly have any of the above mentioned symptoms whether it is just one of the symptoms, or a combination of them. Your doctor will be able to figure out if Addison's disease is the cause so that a proper treatment method can be laid out.
Why It Happens
There are actually two different types of the disease. If the person has primary adrenal insufficiency, it means the issue is the adrenal glands. Meanwhile if they are diagnosed with secondary adrenal insufficiency, it means the issue is that the adrenal glands are underperforming due to a problem elsewhere in the body. This can mean there is a problem with the person's pituitary gland.
Primary Adrenal Insufficiency Causes
In the case of primary adrenal insufficiency the cause is most often autoimmune disease. In fact, this is the case in 70% of the cases of Addison's disease. In these cases the body begins to fight the adrenal glands due to an immune system mistake. What ends up happening is that the outer area of the glands is completely ruined. Apart from autoimmune disease, there are other illnesses that can cause primary adrenal insufficiency, which include HIV, tuberculosis, some fungal infections as well as cancer cells spread to adrenal glands.
Secondary Adrenal Insufficiency Causes
The causes of secondary adrenal insufficiency are typically a problem with the hypothalamus or the pituitary gland. These are both found in the center of the brain and each is responsible for controlling the production of hormones.Over-usage of steroid hormones such as prednisone can also cause this condition. In rare cases, pituitary gland damage from radiation or surgery and pituitary gland tumors may be the causes.
Diagnosing Addison's Disease
Diagnosis is an important step and can be done by speaking with your doctor. To begin with, your medical history will be discussed. There are also a variety of tests that can be performed. Here's a look at them.
- Imaging Tests - A doctor may request for an MRI scan or a CT scan. The MRI scan will be taking a look at your pituitary gland, whereas the CY scan will look at the size of your adrenal glands, your abdomen, and other areas.
- ACTH Stimulation Test - In this test the person will be given a shot of ACTH, a synthetic form of it. The person's cortisol level will be taken both before and after the shot to see what your adrenal gland does after ACTH is sent into the body.
- Blood Test - A blood test may be performed to take a look at your cortisol, potassium, and sodium levels.
- Insulin-Induced Hypoglycemia Test - Although not as common, this test may be recommended by the doctor. It will test for secondary adrenal insufficiency due to pituitary disease. The test focuses on your cortisol and blood sugar levels.
How Can It Be Treated?
Treatment is a key part of Addison's disease, especially since the disease can be life-threatening. Treatment usually is determined by the actual cause of the disease, as there are different routes to take.
- Medications: Typically a person won't have to remain in the hospital in order to receive care; instead they will be put on medication they can take at home. As well they will need to perform check-ups on a regular basis to be sure the medication is doing its job.The drugs that are usually prescribed are glucocorticoids. These will need to be taken forever in order to be effective.
- Hormone replacement therapy is sometimes used. This type of therapy can prove to be quite beneficial as long as the person follows the doctor's orders on dosage information.
- For Addisonian crisis patients, then they usually need to be admitted into the hospital immediately. Doctors will then proceed with sugar and fluid replacement as well as hydrocortisone injections.
Warning
The key with the medications is that you take exactly the amount prescribed at the intervals that have been given to you. If the person veers off-course with their treatment, there can be some rather serious health side effects.
It's also recommended to carry with you extra medication at all times, just in case. You can wear a medical alert bracelet or carry a card, and you can even carry with you an injectable corticosteroid, which is key in an emergency situation.
