The lymph nodes at the back of the throat are known as the tonsils. They are involved in tackling infections entering the body through the nose and mouth. Sometimes swelling in the tonsils can occur, on one side or both. A swollen tonsil on one side is most frequent in children aged 2-15. They may also suffer from headache, sore throat, fever, hoarse voice, and difficulty swallowing. The tonsils appear red, and may have yellow or white spots.
Possible Causes of Swollen Tonsil on One Side
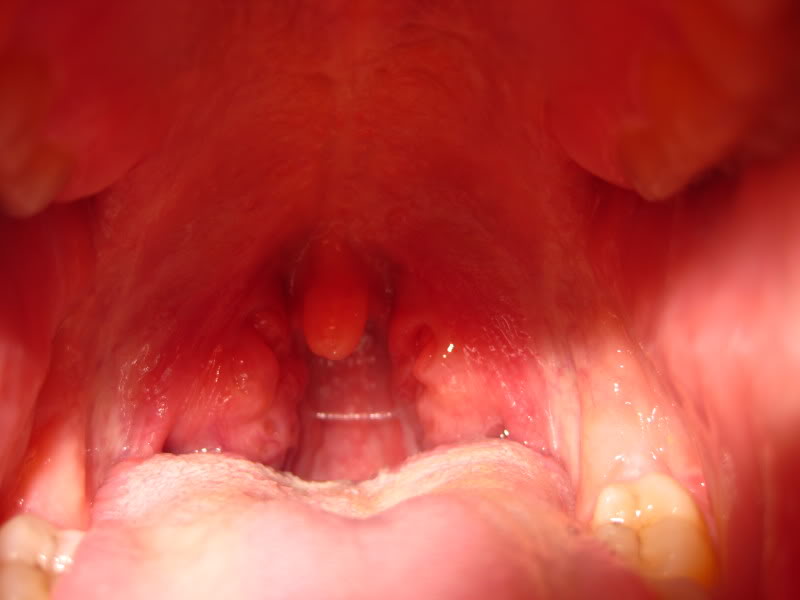
There are many possible reasons for this condition. In this article, we will outline three of the most common causes, and indicate some of the other symptoms you should look out for. However, for an exact diagnosis, you’ll need to see a doctor.
1. Tonsillitis
If the tonsils are infected, they become inflamed and swell. This condition, termed tonsillitis, is most commonly seen in children, and can recur frequently.
Causes
Tonsillitis is caused by bacterial and viral infections, most commonly Streptococcus (strep) bacteria. It can also be due to:
- Influenza virus
- Epstein-Barr virus
- Enterovirus
- Adenovirus
- Parainfluenza virus
- Herpes simplex virus
- Enteroviruses
Symptoms
Tonsillitis is characterized by inflamed, swollen tonsils, which can grow large enough to cause airway obstruction. You may also experience:
- Bad breath
- Sore throat
- Reddened tonsils, with a yellow or white coating
- Neck and jaw gland swelling
- A scratchy or weak voice
- Painful ulcers and blisters on the throat
- Trouble breathing through the mouth and swallowing
- Bad breath
- Headache
- Earache
- Decreased appetite
- Fever and chills
Children with tonsillitis also frequently suffer from vomiting, nausea, and abdominal pain.
Treatment
Tonsillitis treatment is mostly determined by the cause, which can be identified by taking a throat swab and sending this for lab testing. Bacterial infection may be detected, but if not, the patient is assumed to have a viral infection. Alternatively, physical examination and medical interview may indicate a bacterial infection.
Bacterial tonsillitis is usually treated with antibiotics. You need to take the whole course, even if symptoms improve, to prevent relapse. By contrast, viral infections are often left to resolve by themselves.
You can also take the following steps to relieve symptoms:
- Gargling with salt water
- Sucking on throat lozenges containing anesthetic compounds, such as benzocaine
- Using over-the-counter painkillers
- Relieving pain in the throat with either very cold or warm drinks
- Using a cold-mist humidifier or vaporizer
- Choosing smooth foods that won’t irritate your throat, such as ice cream, soups, and jelly
In recurring tonsillitis, or if the enlarged tonsils are causing great difficulty swallowing or breathing, your doctor may recommend complete removal of the tonsils.
2. Strep Throat
Another possible cause of swollen tonsil on one side is strep throat. Patients with strep throat have throat pain and inflammation, caused by Streptococcus bacterial infection. Although it can affect people at any age, it is most common in children aged between 5 and 15. It is spread from person to person by coughing and sneezing.
Symptoms
Strep throat can vary in the type and severity of symptoms, which usually develop within five days of bacterial exposure. The following symptoms are characteristic of strep throat:
- Sore throat
- Fever
- Trouble swallowing
- Swollen neck glands
- Decreased appetite
- Headache
- Chills
- A reddened throat with white patches
Treatment
Doctors usually prescribe antibiotics to deal with strep throat, and limit the spread of Streptococcus bacteria. Although several different kinds of antibiotic can be prescribed, amoxicillin and penicillin are most common. It can be tempting to stop antibiotic medication when symptoms have improved, but this can trigger a relapse and promote antibiotic resistance, so make sure you take the entire course.
There are also many home remedies you can use for strep throat to ease your symptoms. These include:
- Throat lozenges
- Gargling with salt water
- Cold-mist humidifiers
- Over-the-counter painkillers, such as aspirin and ibuprofen
- Warm drinks, such as herbal teas and lemon water
- Cold drinks to numb a sore throat
3. Peritonsillar Abscess
Peritonsillar abscess, commonly known as quinsy, is an uncommon, but possibly serious consequence of tonsillitis, which could be the cause for swollen tonsil on one side. This is where pus collects between the throat wall and tonsil, forming an abscess. It’s a result of the bacterial infection spreading from the tonsil to the surrounding region of the mouth. Quinsy is most frequently seen in young adults and adolescents, and can occur more than once.
Symptoms
Quinsy is suspected if patients have the following symptoms:
- Bad breath
- A swollen mouth or throat
- Trouble opening the mouth
- Painful and difficult swallowing, which can cause drooling
- An intensely painful throat on one side, which seems to be worsening
- Vocal changes or trouble speaking
- Pain in the ear on the affected side of the head
- Headache
- Trouble breathing
- High temperature and fever, although this often resolves prior to the abscess forming
- A general run-down feeling
Treatment
The pus within the abscess will often need to be drained by lancing the abscess with a needle. This can usually be performed in the doctor’s surgery. In addition, a course of antibiotics is normally prescribed. In case of recurring quinsy, the tonsils may need to be removed.
When to See a Doctor for Swollen Tonsil on One Side
If you see any of the following, seek medical help:
- Sore throat that has not disappeared after 48 hours, is accompanied by swollen, tender glands, or occurs with a rash
- No improvement after two days strep antibiotic treatment
- Trouble swallowing or breathing
- Fever over 101°F (38.3°C) or lasting over two days
- Cola-colored urine for over a week – this may be post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis – a type of kidney inflammation
- Painful or swollen joints, breathlessness, fever, or rash. This can occur even three weeks after strep, and suggests rheumatic fever.
