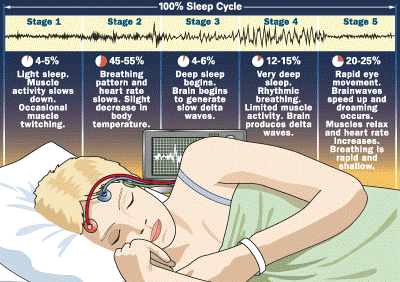
Sleepwalking, or parasomnia, is a behavior occurs during slow wave sleep--the deepest stage of dreamless sleep, or non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep. Those who experience parasomnia will usually sleepwalk early in the night, usually around one-to-two hours after going to sleep. A sleepwalking episode can usually last several minutes or longer. Children are more likely to sleepwalk, although it also can happen in adults. Parasomnia can happen occasionally or frequently, and the chances of episodes occurring are exacerbated by sleep deprivation.
Why Do People Sleepwalk?
1. Genetic Factor
Genetics are thought to play a huge role in sleepwalking, meaning that if one of your parents experiences parasomnia, you are more likely to experience episodes. If both parents have experienced parasomnia, then one’s chances of sleepwalking are even greater.
2. Medical Conditions and Sleep Disorders
Certain medical conditions can make sleepwalking more common among individuals. These include:
- Insomnia
- Restless legs syndrome
- Obstructive sleep apnea or other sleep-related breathing conditions
- Depression
- Hyperthyroidism
- Migraines and head injuries
3. Anti-Depressants, Sleeping Pills, and Other Medications
Some medications can increase the likelihood of sleepwalking; these include:
- Some prescription sleeping aids like Zolpidem
- Some over-the-counter sleeping aids which contain anti-histamine diphenhydramine
- Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRI) anti-depressants such as Paxil, Prozac, Zoloft, or Celexa
- Other medication used to treat mental health, such as lithium or chlorpromazine
4. Other Factors
Other factors which can cause one to sleepwalk include:
- Tiredness
- Stress
- Sleep deprivation
- Fatigue
- Anxiety
- Sleeping in a new place
- Recreational drugs
- Alcohol
How to Tell If Someone Is Sleepwalking?
After knowing the answer to why do people sleepwalk. It would be wise to also comprehend how to tell if someone is sleepwalking. Sleepwalkers usually have their eyes open but they will not be fully conscious and may have a blank facial expression. Other signs to look out for include:
- You may be able to converse with them slightly, but they won’t make normal eye contact with you. And they will likely have no recollection of what happened when they wake up.
- Some individuals may sleepwalk for just a few seconds, while others may sleepwalk for 30 minutes or longer.
- Some sleepwalkers may return to their bed as though nothing had happened, others may wake up in a different room, feeling understandably confused.
One should also note that parasomnia may be confused with a different sleep disorder, known as REM sleep behavior, whereby individuals act out what is occurring in their dreams.
Is Sleepwalking a Serious Problem?
Generally speaking, sleepwalking is not something one should worry about, but it is important to take precautions to ensure that they do not fall, walk out of the house, or into objects.
Should You Wake Up a Sleepwalker?
It can be quite tempting to wake someone who is sleepwalking, but this is not the best option at such a time. Instead, you should try to guide them back to their bed without waking them. If they resist returning to their bedroom, you should allow them to sleepwalk but ensure to keep an eye on to make sure that no harm comes to them. One should only awake a sleepwalker if it is unequivocally necessary, and this should be done gently so as not to startle them. Keeping them safe should be of the upmost importance.
How to Keep a Sleepwalker Safe
There are numerous things you can do to help keep a sleepwalker safe. These include:
- Lock windows and doors throughout the home.
- Keep car keys out of reach.
- Avoid letting the sleepwalker sleep on the top of bunk bed.
- Remove any breakable, sharp, and dangerous objects from the vicinity of the sleepwalker.
- Remove obstacles which may cause a sleepwalker to fall or stumble.
- Equip safety gates or doors at the top of stairs.
When to Seek Medical Help
After knowing the exact answer to why do people sleepwalk, it is also important to understand when sleepwalking can become a problem. As previously stated, occasional sleepwalking is not something to worry about, however, one should seek medical help if any of the following applies:
- Sleepwalking episodes occur often (more than 1-2 times a week).
- Sleepwalking is putting the individual or those around them in danger.
- Sleepwalking causes great embarrassment to the individual who is doing it, or great disruption to those who they live with.
- Sleepwalking happened for the first time in one’s adult life after having not sleepwalked as a child.
- Sleepwalking continues through adolescence and into the teenage years.
