The cause of diabetes is either incorrect use of hormone insulin by your body or not producing it in sufficient amounts, both of which affect levels of blood sugar adversely. Can diabetes affect health of your joints? Diabetes has an effect on both the circulation and nerves, which may lead to pain in joints and other disorders in multiple areas of your body. While mentioning diabetes complications, joint disorders get sidelined by the likes of kidney disease and retinopathy but we should take them seriously.
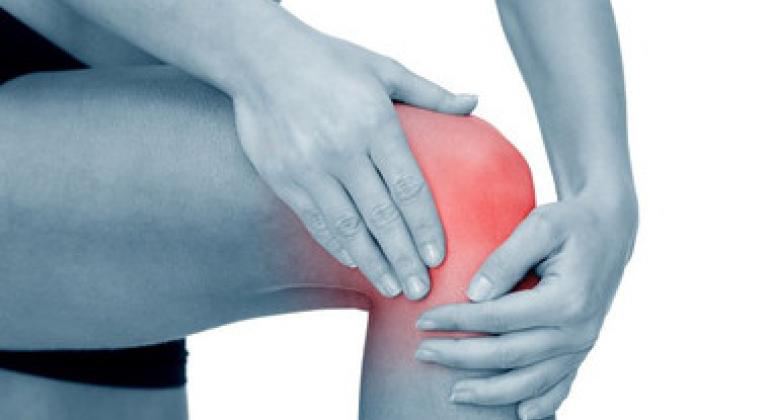
How Are Diabetes and Joint Pain Related?
Charcot’s Joint
Charcot’s joint results when nerve damage due to diabetes causes a breakdown of a joint. This condition is also referred to as neuropathic arthropathy and is present in ankles and feet of diabetics. Damage to nerves is commonly present in diabetics and this results in Charcot’s joint. Numbness results due to nerve damage. Individuals who walk with numbness in their feet are more prone to twist and cause injury to their ligaments. This puts pressure on joints, causing their wear and tear. Due to severe damage foot deformities may occur.
You may prevent bone deformities by early intervention. Symptoms and signs of Charcot’s joint are:
- Pain in joints
- Redness or swelling
- Numbness
- Joint is hot to touch
- The appearance of feet changes
In case your physician finds that your pain in joint is due to Charcot’s joint, you should limit using the affected joint so as to prevent deformities of bone. If you develop numbness in feet, wear orthotics to provide additional support. Hence, diabetes and joint pain are directly related if you have Charcot’s joint.
Type 2 and OA
OA or osteoarthritis is among the most common type of arthritis. It may occur due to or worsened by excessive weight and this is common in people suffering from diabetes type 2. Diabetes may not directly lead to OA, but being obese raises the risk of developing both OA and diabetes type 2.
OA results from wear and tear of the cartilage present between the joints. This results in rubbing of bones leading to joint pain. Though wear and tear of joint occurs naturally with age, the process is increased by excess body weight. The symptoms may include swelling of joints and difficulty moving your limbs. The commonly affected joints are the knees and hips.
To treat osteoarthritis, the most effective method is to shed weight as extra weight puts pressure on your bones. Diabetes also becomes difficult to control due to obesity. Hence, shedding weight will not only relieve your joint pain but also control other symptoms of diabetes.
The Arthritis Foundation states that by shedding 15 pounds, you may reduce your knee pain by half. Regular exercise also helps in lubricating your joints; thereby, you will feel pain less. Your physician may prescribe medicines to relieve pain when discomfort due to osteoarthritis becomes unbearable. In more severe cases, knee replacement surgery may be needed.
Type 1 and RA
RA or rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune condition that is characterized by inflammation of the joints present as redness and swelling of joints. The exact cause of rheumatoid arthritis is not known. A presence of autoimmune diseases in the family increases your risk of developing RA.
Diabetes type 1 is also a type of autoimmune disease; therefore, there exists a link between diabetes and joint pain due to RA. Inflammatory markers are also shared by the two conditions. Both diabetes type 1 and RA results in raised levels of C-reactive protein and interleukin-6. Certain arthritis medicines may help in the reduction of these levels and hence, improve both diseases.
Primary symptoms of RA are swelling and pain. Symptoms may get flared up or get better without any warning. No cure is present for autoimmune illnesses such as RA; hence, the aim of therapy is to decrease inflammation. Newer drugs for RA are:
- Enbrel (etanercept)
- Humira (adalimumab)
- Remicade (infliximab)
The above 3 medicines may prove beneficial in reducing the risk of diabetes type 2. Diabetes type 2 is accompanied with inflammation and these medicines help to manage that. In a study, the risk of developing diabetes type 2 was less in individuals who were taking these medicines.
Outlook
The key for relieving joint pain related to diabetes is to diagnose it early. Though the conditions leading to pain have no cure, the discomfort and pain can be minimized by using available treatments. Call your physician if you have swelling, pain, numbness or redness in your legs and feet. These symptoms of diabetes and joint pain should be taken care of as early as possible. In case you suffer from diabetes or you are at risk of developing diabetes, talk to your physician regarding your risk factors of joint pain.
How to Relieve Diabetic Joint Pain
Below are the things that you can do to treat and prevent problems of joint:
1. Stretching helps keep your tendons and muscles aligned and relaxed so they can move as required. You can ask a trainer or a physical therapist what stretches you can do.
2. Perform resistance training for strengthening of muscles surrounding the joints.
3. Aerobic exercises such as swimming or walking helps in improving function of hips and knees. Water exercises are also great for people who have painful joints. Similarly bike riding is a no impact exercise and may be done when your joints hurt.
4. Make variation in your activities. For example, while hanging clothes, stop in between and rest for some time and then resume the activity. Don’t do high-impact, repetitive activities such as jumping, running, high-impact aerobics and tennis.
5. Improve your blood sugar levels as it helps in not getting your joints coated with sugar and stiff.
6. Rest your joints if they are painful so that they can heal properly.
7. Shed some weight as it may help in reducing your joint pain.
8. Use cold and heat therapy. Icing your joints post activity for 12-15 minutes cools them and decreases inflammation. Applying hot pack to the joints during rest may help them to move and heal.
9. Keep the affected joints particularly hands and knees warm under wraps and gloves especially in cold climate.
10. Medicines such as acetaminophen (Tylenol) or ibuprofen (Advil or Motrin) may help relieve inflammation and pain. Other stronger, prescription drugs are also available in case you need them.
11. You can try supplements under the guidance of your physician. Certain supplements such as glucosamine, vitamin D, chondroitin and omega-3 fish oils are found to be beneficial in joint pain. MSM (methylsulfonylmethane) has also been shown to decrease joint pain in studies. Ginger extract also helps with joint stiffness and pain. Topical creams that contain capsaicin reduce joint pain.
12. You can use supportive devices such as braces for arthritis in knees, orthotics to support foot and supportive shoes. Other supportive devices are also available for pain in joints of hands.
13. Quit smoking. Smoking puts stress on connective tissue of joints resulting in joint pain.
14. Acupuncture also helps in reducing joint pain.
