Amniotic fluid is a liquid of a clear or a little yellow color that is found in the uterus of pregnant women, which can becalled liquor amnii. The amniotic liquid surrounding the fetus is quite essential to the baby's development.
To estimate the volume of amniotic fluid within the uterus, the amniotic fluid index is used, which is measured against the amniotic fluid index chart.
Amniotic Fluid Index Chart
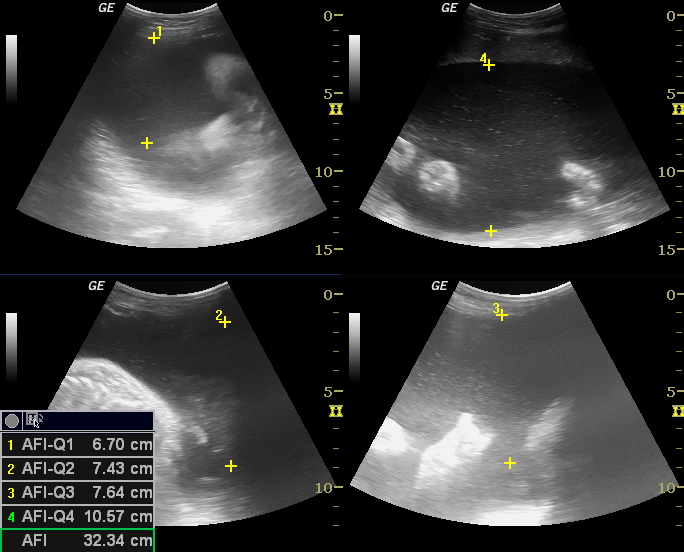 When a woman is pregnant, she often undergoes a series of ultrasound examinations to attain a fetal biophysical profile. The amniotic fluid index (or AFI) is used to estimate the well-being of the fetus by doing an ultrasound of the uterus to estimate the levels of amniotic fluid levels in the uterus.
When a woman is pregnant, she often undergoes a series of ultrasound examinations to attain a fetal biophysical profile. The amniotic fluid index (or AFI) is used to estimate the well-being of the fetus by doing an ultrasound of the uterus to estimate the levels of amniotic fluid levels in the uterus.
There areseveral approachesto test; the most commonly used methods are the four-quadrant techniqueand the 'single deepest pocket'. The amniotic fluid index chart shows the average volume of amniotic fluid in a pregnant woman based on gestational agein millimeter.
|
Amniotic Fluid Index Chart Percentile Values | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Week |
2.5th |
5th |
50th |
95th |
97.5th |
|
16 |
73 |
79 |
121 |
185 |
201 |
|
17 |
77 |
83 |
127 |
194 |
211 |
|
18 |
80 |
87 |
133 |
202 |
220 |
|
19 |
83 |
90 |
137 |
207 |
225 |
|
20 |
86 |
93 |
141 |
212 |
230 |
|
21 |
88 |
95 |
143 |
214 |
233 |
|
22 |
89 |
97 |
145 |
216 |
235 |
|
23 |
90 |
98 |
146 |
218 |
237 |
|
24 |
90 |
98 |
147 |
219 |
238 |
|
25 |
89 |
97 |
147 |
221 |
240 |
|
26 |
89 |
97 |
147 |
223 |
242 |
|
27 |
85 |
95 |
146 |
226 |
245 |
|
28 |
86 |
94 |
146 |
228 |
249 |
|
29 |
84 |
92 |
145 |
231 |
254 |
|
30 |
82 |
90 |
145 |
234 |
258 |
|
31 |
79 |
88 |
144 |
238 |
263 |
|
32 |
77 |
86 |
144 |
242 |
269 |
|
33 |
74 |
83 |
143 |
245 |
274 |
|
34 |
72 |
81 |
142 |
248 |
278 |
|
35 |
70 |
79 |
140 |
249 |
279 |
|
36 |
68 |
77 |
138 |
249 |
279 |
|
37 |
66 |
75 |
135 |
244 |
275 |
|
38 |
65 |
73 |
132 |
239 |
269 |
|
39 |
64 |
72 |
127 |
226 |
255 |
|
40 |
63 |
71 |
123 |
214 |
240 |
|
41 |
63 |
70 |
116 |
194 |
216 |
|
42 |
63 |
69 |
110 |
175 |
192 |
Techniques and Values of Amniotic Fluid Index Charts
Technique
Using the umbilicus and the linea nigra as horizontal and vertical axis, an imaginary divide is created inside the uterus, which is split into four quadrants. The deepest pocket without fetal parts or umbilical cord is then measured in millimeters or centimeters vertically. The sum of the four quadrants, in millimeters or centimeters, is amniotic fluid index. Usually, the normal value of amniotic fluid index varies from 50 mm to 250 mm (or 5 cm to 25 cm).
Values
Normal AFI varies from 80 mm to 180mm. An average AFI level is 80 mm to 140 mm when you are in your 20 weeks to 35 weeks of pregnancy. After 35 week, AFI levels usually begin to reduce.
The AFI < 50-60 mm is assumed as oligohydramnios, while AFI >250mm is assumed as polyhydramnios. With the pregnancy process going on, the AFI values are changing, and the percentile for fetus age is usually referred as the cutoff value.
What If I Have Abnormal Amniotic Fluid Levels?
If there are high amounts of amniotic levels in a mother's uterus then it is known as polyhydramnios, whereas having small amounts of amniotic fluid can lead to oligohydramnios. With the amniotic fluid index chart above, you will wander what are the possible complications along with oligohydramnios and polyhydramnios?
Low Amniotic Fluid Levels
Having low levels of amniotic fluid inside the uterus during pregnancy can lead to numerous problems, which include miscarriage, premature birth, and stillbirth. There are often no symptoms experienced by the mother, except for their belly not growing in alignment with their duration of pregnancy, being smaller than it should.
High Amniotic Fluid Levels
The symptoms of polyhydramnios for this include edema, difficulty breathing, and excessive weight gain. Polyhydramnios can lead to many of the same complications as oligohydramnios, and the extra fluid can leak through the vagina in rare instances. Polyhydramnios can also lead to certain congenital complications, including Down’s syndrome.
Possible Treatments for Polyhydramnios and Oligohydramnios
Unfortunately, effective treatments for polyhydramnios and oligohydramnios are limited. In some cases of oligohydramnios, extra fluid has been added to the mother's amniotic sac in an effort to increase amniotic fluid levels within the uterus. The opposite is done in treatment of polyhydramnios, where a syringe is inserted into the amniotic sac to drain excess fluid. If needed, this option can be done more than once.
If the cause of the condition is known, then other treatmentsmay be applied. If a fetal bladder obstruction is the cause of oligohydramnios, a small tube can be placed in the bladder to allow the fluid to flow into the amniotic sac.
Pharmaceutical drugs are sometimes prescribed to treat polyhydramnios, such as indomethacin, but concerns have been raised over implications to the unborn baby and other side-effects.
