A fracture denotes a partial or complete break in a bone. Thus, ankle fracture refers to breaks in one or more ankle bones. Two leg bones (tibia and fibula) and one foot bone (talus) comprises the ankle joint. A fracture in the leg portion of the ankle joint may lead to a serious situation, resulting in an ankle shift due to bone instability. Trauma or injury to the ankle joint can lead to ankle fractures.
What Is An Avulsion Fracture (Ankle)?
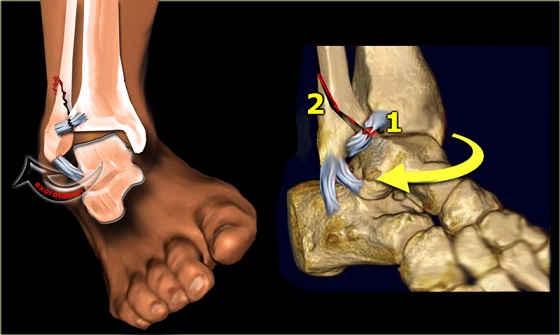 The term refers to a severe condition resulting from an avulsion fracture in the ankle joint. The term ‘avulsion’ is used to indicate the rupture of the ligament at its point of attachment to the bone. When subjected to significant stress or strain, a ligament can rupture at its mid-substance region or at its point of attachment to the bone. If the external force is powerful enough, small pieces of bones may also be pulled out along with the ruptured ligament at the boney interface resulting in an avulsion fracture.
The term refers to a severe condition resulting from an avulsion fracture in the ankle joint. The term ‘avulsion’ is used to indicate the rupture of the ligament at its point of attachment to the bone. When subjected to significant stress or strain, a ligament can rupture at its mid-substance region or at its point of attachment to the bone. If the external force is powerful enough, small pieces of bones may also be pulled out along with the ruptured ligament at the boney interface resulting in an avulsion fracture.
Avulsion fractures can occur in any part of the body but they occur more frequently in the ankle, elbow and hip joints since these joints are more often subjected to stressful movements. Even though avulsion fractures can affect anyone, children and athletes have a higher susceptibility to avulsion fractures.
Symptoms and Causes of Avulsion Fracture in Ankle
Due to the overlapping symptoms, avulsion fractures are often misdiagnosed as sprains. The ankle avulsion fracture is usually accompanied with the following symptoms:
- Immediate and speedy swelling of the ankle joint
- Bruising
- Any attempt to make a forceful, twisting movement of the ankle leads to a sensation of pain
- Ankle movement becomes difficult
- Weight bearing becomes arduous
- Persistence of swelling
- Tenderness to touch
The best way to distinguish between a condition of an avulsion fracture ankle and a less critical ankle strain is to perform an X-ray or MRI examination.
Causes
Avulsion fractures in the ankle joint may result from any activity that generates sufficient force to create an avulsion fracture. Athletes, especially football, basketball and soccer players, are more prone to suffer from this condition.Athletic activities involve a high degree of muscle movements, and the strong muscle contractions in such activities can result in pulling ligaments and tendons away from the bone, leading to avulsion fractures.
Usually, neurological limitations restrict the common man from exerting muscle contractions that are strong enough to lead to avulsion fractures. However, with practice, athletes learn to overcome such limitations to perform better in their sport. This renders them more likely to suffer from avulsion fractures.
How Can Avulsion Fracture Ankle Be Treated?
There is not much difference between the treatment of the ankle avulsion fractures and ankle sprains. The nature of treatment depends on the acuteness of the condition. Invasive procedures are usually not required in most cases of avulsion fractures.
1. RICE
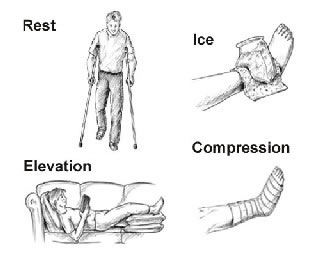
This is the most common treatment module for ankle avulsion fractures. RICE involves the combination of rest, ice (to reduce the swelling and inflammation), compression of the joint with the help of bandages and elevation of the fractured ankle.
2. NSAID
NSAIDs or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can also be prescribed for the treatment of avulsion fractures. Treatment with such drugs and ice will suffice if the injury is mild. For example, if the chips of the bone lost in the fracture are too small to be a cause of worry, or the bone pieces are not completely detached from the rest of the bone, then treatment with just ICE and NSAID may be good enough to revert to the original condition.
3. Casting
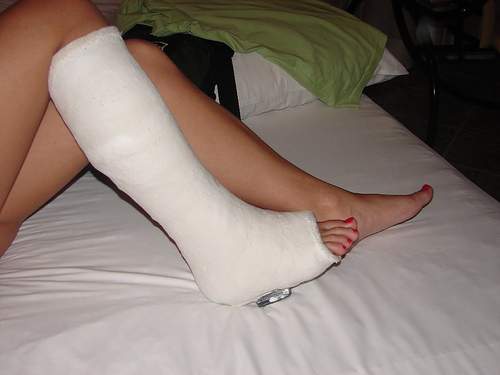
When the avulsion fracture is more severe and the bones have been dragged more than a few centimeters out of their original position, then resorting to surgery or casting may be the only option left for treatment of your avulsion fracture ankle.
In acute cases of ankle avulsion fractures in children, the need of immobilization of the joint for 6-8 weeks with the help of casting may be deemed necessary. After the damaged area is completely healed, a patient needs to initiate a rehab program comprising of specialized stretching and strengthening exercises that will allow the patient to gradually recover back to normal activity. The rehab exercises are extremely important to bring back movement and flexibility in the affected joint.
Rehabilitation for Avulsion Fracture Ankle
Rehabilitation to recover an avulsion fracture must be done following proper instructions to avoid further damage to the newly recovered region. Every individual’s response to treatment and rehab procedures varies. Thus, physiotherapists need to individualize such treatments.
The rehabilitation program to recover from an avulsion ankle fracture usually involves three significant stages.
Stage 1 (The Acute Phase)
The aim of this phase of treatment is the reduction of some symptoms of the fracture such as pain and swelling and preventing muscular atrophy in and around the affected region. The phase starts two weeks post-operation or cast removal. This stage involves adoption of passive movement exercises and crytherapy.
Stage 2 (The Recovery Phase)
If the patient responds well to the first phase of treatment and the aims of the first phase have been achieved to a considerable extent, it is time to launch the second phase of treatment. This usually occurs three to four weeks postoperatively and demands the patient to perform some specialized exercises with the help of trained instructors.
Theraband is used for exercises that restore motion and strength in the affected region, while proprioception exercises involve a biomechanical ankle platform setup. Patients should be advised to use the least resistant band at the beginning of the second phase. Towards the end of the phase, patients must learn to use a wobble board and start performing closed kinetic chain activities such as walking and loading.
Stage 3 or (The Functional Phase)
This phase leads to full recovery from the avulsion fracture ankle condition and is initiated 6-8 weeks post-operation. This phase employs activities that increase neuromuscular co-ordination and powers the lower extremity complex system.
