Hodgkin's disease refers to a blood cancer or lymphoma that originates from the lymphatic system. The function of the lymphatic system is to enable the immune system to resist infections and remove wastes. The major types of lymphoma include Hodgkin's and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Hodgkin's disease, discovered by Dr. Thomas Hodgkin, is also referred to as Hodgkin lymphoma, Hodgkin disease or Hodgkin's lymphoma.
Symptoms of Hodgkin's Lymphoma
People suffering from Hodgkin's lymphoma many experience different symptoms at different stages of the disease. The main symptoms include:
- Lack of appetite
- Frequent chills and fever
- Excessive sweating especially at night
- Swollen glands and lymph nodes in the armpits and neck
- Fatigue
- Itchiness throughout the body
- Painful lymph nodes after alcohol consumption
- Breathing difficulties, chest pain and coughing when chest lymph nodes swell
- Losing weight
- Skin flushes
- Pain in the ribs if the spleen or liver swells
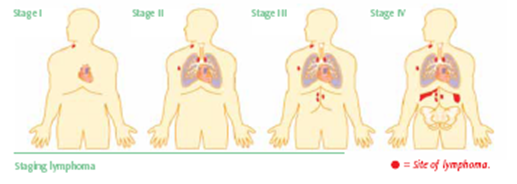
Stages of Hodgkin's Lymphoma
1st Stage
At this stage, all lymphoma cells appear in a single lymph node group. For instance, they may be at the lymph nodes of the armpit or neck. In some rare cases, the disease starts in other body part other than a lymph node; in this case, lymphoma cells only exist in that one part.
2nd Stage
Lymphoma cells appear in two groups of lymph nodes in the same side of the diaphragm. In other cases, the cells appear in one part of an organ or tissue and the lymph node close to that organ, which are in one side of the diaphragm. Lymphoma cells might appear in different groups of lymph nodes that are on the same side of the diaphragm.
3rd Stage
Here the lymphoma cells spread to lymph nodes on all sides of the diaphragm. The cells may also appear in the spleen or one organ or tissue part close to those groups of lymph nodes.
4th Stage
In this stage, the lymphoma cells spread to different parts of one tissue or organ. They may spread to one organ (like the bone, lung or liver) and lymph nodes on the opposite of the diaphragm.
Causes of Hodgkin's Lymphoma
Hodgkin's lymphoma occurs when an infection-fighting B cell mutates in its DNA. The mutation causes cells to divide at high rate and live longer than normal cells. Consequently, the lymphatic system has many abnormal and oversized B cells which push out healthy cells and lead to signs and symptoms of Hodgkin disease.
Risk Factors of Hodgkin's Lymphoma
The main risk factors include:
- HIV infection
- Family history –individuals with a parent, twin or same sex sibling who have suffered from the disease
- Individuals between 15-35 years and 50-70 years
- Growing up with few siblings, playmates, in early birth order, or in a single family because the lack of exposure to viral diseases and bacteria at early age.
How to Diagnose Hodgkin's Lymphoma
Hodgkin disease is diagnosed using the following tests and procedures:
- Physical examination: A doctor may check the armpits, neck and groin to look for swollen lymph nodes. The doctor will also check for swollen liver or spleen.
- Blood tests: A sample of your blood is screened for signs of cancer
- Imaging tests: These include positron emission tomography (PET), computerized tomography (CT) scan and X-ray.
- Surgical procedure on swollen lymph nodes: Your doctor may conduct a minor surgery to get some tissue from a swollen lymph node to test for Hodgkin disease. Reed-Sternberg cells in these lymph nodes are a sign of the disease.
- Bone marrow testing: An alternative way of diagnosing Hodgkin lymphoma is conducting a biopsy of the bone marrow. The procedure involves removing a small amount of blood, bone marrow and bone with a needle, and then screening them for signs of cancer.
How to Treat Hodgkin's Lymphoma
The treatment options for Hodgkin’s lymphoma vary depending on the stage of the disease and personal preferences. The main treatments options are discussed below.
1. Chemotherapy
This option involves killing lymphoma cells with chemicals. The drugs used in chemotherapy diffuse into the bloodstream and spread to almost all body parts. At the early stage of the Hodgkin disease, doctors combine chemotherapy with radiation therapy which comes after chemotherapy. At advanced stages, chemotherapy is done either alone or with radiation therapy.
Chemotherapy drugs are administered in several combinations through a vein or in pill form. Side effects of chemotherapy vary depending on the drugs. They may include hair loss, nausea, cancers like leukemia, heart damage, infertility and lung damage.
2. Radiation
Radiation therapy involves killing cancer cells using high-energy beams like X-rays. Radiation therapy may be administered alone or with chemotherapy for classical Hodgkin disease. It is used alone in early stages of lymphocyte-predominant type of Hodgkin's lymphoma.
In a radiation therapy session, energy beams are directed on your lymph nodes or to areas prone to the disease as you lie on a table. The session may be long or short depending on the disease stage.
Some of the side effects of radiation therapy include hair loss, redness, fatigue, infertility, heart disease, thyroid problems, strokes, and other cancers including lung and breast cancer.
3. Stem Cell Transplant
This treatment involves replacing diseased bone marrow with healthy stem cells. The new cells develop a new, healthy bone marrow. This treatment is recommended when the disease recurs after treatment.
A stem cell transplant uses your blood stem cells which are removed and frozen. The next step in the treatment is intense radiation therapy and chemotherapy. These high dose sessions kill cancerous cells in the affected areas. The final step is injecting thawed blood cells through your veins into your body. These healthy cells will grow a healthy bone marrow.
Survival Rate of Hodgkin's Disease
The introduction of new and better treatment options of Hodgkin's lymphoma has increased survival rates.
The 1-year, 5-year and 10-year survival rates for individuals diagnosed with the disease are 92%, 85% and 81% respectively. The survival rates vary across patients based on their age and stage of the disease. The 5- year survival rates for Stage 1 HD, Stage 2 HD, Stage 3 HD and Stage 4 HD are about 90%, 90%, 80% and 65% respectively.
Since the disease can recur after treatment, your doctor must conduct regular checkups. Ensure that you follow your doctor's instructions during and after treatment. Do not miss any medical appointment when undergoing treatment.