Stroke occurs when blood supply to the brain is disturbed, resulting in loss of proper functioning of the brain. It was also known as cerebrovascular accident or CVA in medical terminology. When the brain cells do not receive blood, they are not able to function properly. This can result in improper functioning of limbs, inability to speak, understand or even see, due to loss in vision. This can happen mostly to one side of the body.
Stroke is an emergency, which can cause permanent damage or even death. It is a leading cause of disability in adults and death as well. The risk factors for it include hypertension, diabetes, smoking, high cholesterol levels, etc. It is important to get diagnosed properly and for that reason we will look at what the nursing diagnosis for stroke is.
How Is Stroke Diagnosed?
Nursing diagnosis for stroke can vary and be done using different techniques. A CT Scan, without using any contrast, MRI scan, Arteriography and Ultrasound using Doppler can be performed. A neurological examination like the Nihss can also be done to diagnose a stroke. The results from imaging technique are used to make a clinical diagnosis of stroke. It helps in finding the sub-type and the cause. Blood tests are not routinely done to diagnose stroke, but they can be done to find the cause of stroke.
Nursing Diagnosis for Stroke
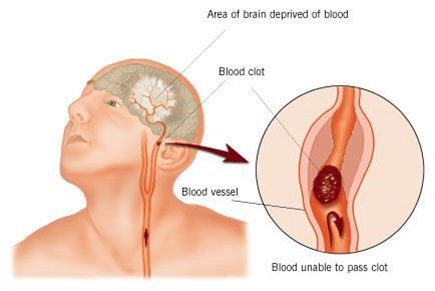
Stroke can make the person require constant care and medical attention as well. We will look at some different nursing diagnosis for stroke:
1. Ineffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion:
This is caused due to Hydrocephalus; in this condition, there is disturbance in the flow, absorption and production of the cerebrospinal fluid in the brain. It can occur in very young babies or in very old people.
Symptoms
- Memory loss
- Change in level of consciousness
- Restlessness
- Change in vital signs
- Emotional, sensory, intellectual and language deficit
Nursing Intervention
- Check for decrease in cerebral perfusion and increased ICP.
- Compare neurological status with baseline frequently.
- Check blood pressure in both arms, heart rate, respiration, pupil for size, shape and reactivity to light.
- Give lot of bed rest, keep head in elevated position, supplement oxygen as required.
- Administer medications as required.
2. Impaired Physical Mobility
This happens when the neuromuscular system is involved, leading to weakness, paralysis either flaccid or spastic, paresthesia and cognitive impairment.
Symptoms
- Inability to move around
- Lack of co-ordination
- Restricted range of motion
- Reduced strength in muscles and muscle control
Nursing Intervention
- Access the impairment regularly and classify on a 0-4 scale.
- Change position frequently and keep in prone position couple of times in day.
- Use slings or positional aids if possible.
- Inspect skin for reddening, color, edema, etc.
- Teach and help in performing exercise for affected side and use the unaffected part.
3. Impaired Verbal Communication
This occurs when there is impaired cerebral circulation, loss of control of facial or oral muscles, overall weakness and fatigue as well as neuromuscular impairment.
Symptoms
- Unable to speak
- Inability in finding names and words, identifying objects, understanding written or spoken language or writing properly
Nursing Intervention
- Assess the level of dysfunction, whether there is trouble to speak or in understanding and expressing.
- Give and ask to repeat simple instructions, listen and provide feedback.
- Make them write simple sentence, if they are unable, ask them to read.
- Speak slowly and clearly, give adequate time to respond.
- Speech therapist can be consulted and referred to.
4. Disturbed Sensory Perception
This is related to psychological stress which can be triggered by anxiety, changed sensory reception, transmission and integration which can be caused due to neurological deficit or trauma.
Symptoms
- Disorientation to person, place and time
- Over emotional responses, reduced concentration, bizarre thinking, changes in taste and smell
- Unable to point out body parts, change in communication, altered motor coordination
Nursing Intervention
- Observe the patient for behavior like crying, agitation, hallucination, hostility, etc.
- Keep communicating with the patient, while speaking in calm and quiet voice.
- Check perceptions, visual deficits and reorient when possible and required.
- If they are inattentive to body parts, make them see and become aware.
5. Ineffective Coping
This is related to crisis like situations being vulnerable and any other cognitive perpetual changes.
Symptoms
- Not being able to effectively make use of defense mechanisms
- Inability to ask for help
- Disturbed communication
- Unable to meet expectations
- Difficulty in problem solving
Nursing Intervention
- Assess the level of change in perception, find the dysfunction, determine which factors are causing stress.
- Give psychological support, let the patient express feelings and emotions freely.
- Find out support system when dealing with previous problems.
- Check if patient is sleep deprived, unable to cope, feeling withdrawn or lethargic.
6. Self-Care Deficit
The nursing diagnosis for stroke includes this risk of self-care deficit. In this, the patient shows neuromuscular impairment, loss of muscle control, depression and cognitive impairment.
Symptoms
Unable to perform every day activities like bringing food from plate to mouth, to dress up, toileting activities, washing body parts, etc.
Nursing Intervention
- Assess and check the level of deficit.
- Provide assistance only when required, if patient is able to do the task themselves.
- Do not rush, provide adequate time to complete tasks.
- Give self-help devices like extension hooks, drinking straw, shower chair etc.
7. Risk for Impaired Swallowing
This can be caused due to neuromuscular impairment.
Nursing Intervention
- Check and assess the level of paralysis – speech, usage of tongue, coughing episodes, ability to protect the airway.
- Keep a suction pump handy during feeding sessions.
- 30 minutes of rest should be provided before eating.
- Let the patient remain in upright position and ensure oral care is given.
- Place the food in the unaffected part of the mouth and the consistency of the food should be appropriate.
- The food should be at usual temperature and water should be chilled.
8. Knowledge Deficit
This is due to lack of exposure, cognitive limitations, unable to recall information, misinterpretation, etc.
Symptoms
- Asking for information or having misconceptions
- Unable to follow instructions correctly
- Developing complications which could be avoided
Nursing Intervention
- Include the patient and family in discussions and teach the right way for providing support and care.
- Check for signs and symptoms which indicate further follow up or decrease in functioning.
- Give written notes and ask to follow written communication, rather than memory.
- Find out risk factors which can cause harm to general well-being and inform important of balanced diet.
