Posture can be defined as the position that you hold your body parts upright against gravity while lying down, sitting and standing. Proper posture entails training the body to lie, sit and walk in positions that apply the least strain to the ligaments and muscles that support your body when bearing weights or in motion. Proper sitting posture is essential both at work and at home. When involved in any activity, it is important to maintain a back-friendly posture to prevent back pain.
Benefits of Proper Sitting Posture
There are three natural curves on a healthy back:
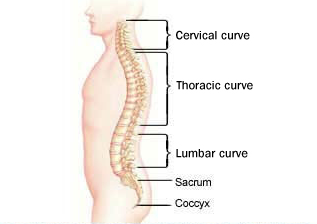
- Cervical curve: a forward or inward curve at the neck
- Thoracic curve: a backward or outward curve on your upper back
- Lumbar curve: inward curve on your lower back
Good posture will ensure that these three curves stay as required, but an improper posture will do the exact opposite. This can result in pain, pulling or stressing the muscles.
Benefits of a proper sitting posture include:
- Contributing to a good appearance
- Preventing muscular and back pains
- Preventing overuse or strain problems
- Less energy is used since the muscles are used effectively thus preventing fatigue
- Preventing the spine getting fixed in abnormal positions
- The ligaments that hold the spine together are less stressed
- Preventing abnormal wearing out of the joint surfaces which is likely to results in arthritis
- Joints and bones are correctly aligned benefiting from proper use of the muscles
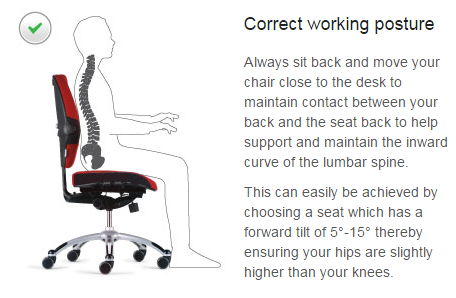
- Your bum should touch the end of the chair with your shoulders back and back straight.
- While seated, all the back curves should be seen. You can use a lumbar roll or rolled up towel to help keep the normal curves.
How to Maintain Proper Sitting Posture
If you are not using a lumbar roll, or back support, here is how to get a proper sitting posture:
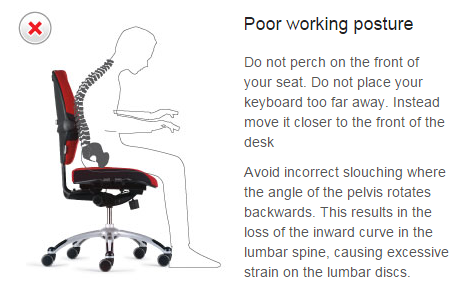
- Slouch completely when seated at the end of the chair.
- Draw your body up and heighten your back as far as possible and hold that position for a few seconds.
- Release the positionabout 10 degrees, there you have a proper sitting posture.
- Let your body weight be evenly distributed on your hips.
- The knees should be bent at 90 degrees, not crossed, at the same height or higher than your hips. If necessary you can use a stool.
- Your feet should be flat on the floor.
- Do not sit in the same position for over half an hour.
- On your work seat, adjust the height of the work station and the seat so that you are closer to your work and lean it towards you. Arms and elbows should rest on the chair arms to relax your shoulders.
- If you are using a seat that pivots and rolls, turn your entire body instead of only your waistwhile sited.
Below is an illustration of improper and proper sitting postures at work:
For more information, please watch the video on how to achieve proper sitting posture at computers to avoid back pain:
Proper Sitting Posture in Cars
Your sitting posture is also crucial when driving. Below is a step-by-step guide for maintaining a proper sitting posture in cars:
- It is much easier if you start with the seat in the wrong position then adjust it to the right position. Push the seat as far back as possible, as low as it can go and tilt it back 30 to 40 degrees.
- Adjust the seat height so that you can see the instruments and the road. Your hips should also be at the same height as your knees. If it’s still low for you, you can add a cushion on the seat or a wedge. This will also lessen the vibrations from the road that have been proven to add injuries. However, you should ensure that you are not too high you end up bending.
- Pull the seat forward enough to step on the pedals without having to move from the back of the seat.
- Ensure the back of the seat is forward so that you are at an angle between 100 to 110 degrees. This will help reduce the pressure applied to the lower discs on your lower back.
- The headrest should be adjusted to the middle of your head. To ensure even back support, adjust the lumbar support to a comfortable position. If your car seat does not have lumbar support, you can add a cushion.
- Adjust the seat cushion to support your thigh without hitting the back of your knees. You should not feel pressure on any particular partsas this can limit blood circulation resulting in distress in the legs.
- Do not adjust the seat to fit the seat belt. Instead, adjust the seat belt to accommodate you.
- Lower the steering wheel and bring it towards you to reduce reach. You strain the neck and upper back less when you your elbows are not reaching upwards and forward.
- The position in which you hold the steering wheel is also important. To relax your shoulders, hold the wheel at the 9 and 3 o’clock positions instead of 10 and 2 o’clock position. Unless you are turning, do not reachacross the body to hold the wheel. For instance, do not hold the right side or top of the wheel using the left arm and vice versa. Maintain your wrist in a straight position while holding the wheel.
