Many parents worry about their children, especially their health. Thyroid problems in children aren’t a rare occurrence, although it isn’t so common to the point of being an epidemic. On average, around five percent of those with hyperthyroidism are under the age of fifteen. Some parents may assume that their child has a thyroid gland problem if they are overweight, although most commonly the excessive weight is due to poor diet and lack of exercise.
What Is The Thyroid?
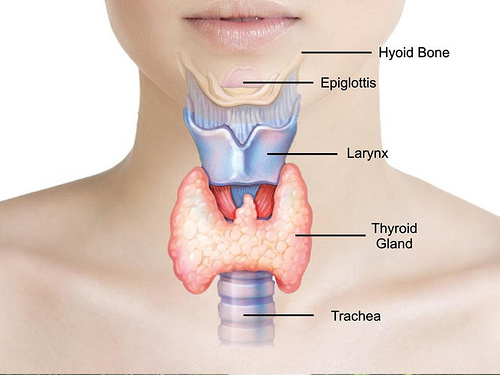
The thyroid is a gland that resides in an individual’s throat, which works to produce hormones
triiodothyronine and thyroxine. These hormones are necessary for numerous important bodily functions.All cells require them to work properly and they are also responsible for determining how quickly the body burns energy, as well as the growth of children.
As mentioned, the thyroid is situated in the throat; more specifically, it resides just under the skin toward the front of the neck, whose shape resembles that of a butterfly. If you wish to find it, place one of your fingers around the Adam’s apple area and another finger at the top of your chest, at your breast bone, the space in between your two fingers will be the thyroid, which should move upwards and downwards when swallowing. The thyroid works to release the right amount of hormones, too many or too little of the hormones being produced can lead to numerous complications.
Symptoms of Thyroid Problems in Children
There are numerous conditions that can affect the thyroid, and the symptoms experienced will vary depending on the condition. Some conditions affecting the thyroid, along with their symptoms, are listed below:
Hypothyroidism
This condition is when the thyroid does not produce a sufficient amount of the hormones it is supposed to. This leads to the hormonal levels dropping, and cause the metabolism to slow. Symptoms include:
- Fatigue
- Hoarse voice
- Difficulty concentrating
- Depressed feeling/feelings of sadness
- Mood swings
- Weakness
- Constipation
- Slowing of natural growth
- Eyes get puffy
- Face and hands become puffy
- Weight gain
- Consistent feeling of being cold
- Skin dryness
- Brittle hair
- Joint and muscle pain/aches
- Decreased heart rate
- Lowered blood pressure
- Higher levels of cholesterol accumulating
- Poor tolerance to exercise
Hyperthyroidism
This condition is when the thyroid is overactive, meaning that the hormones it produces are excessive, which causes an increase in body metabolism. Symptoms of this condition include:
- Feeling of anxiety
- Jitteriness
- Difficulty concentrating
- Fatigue/tiredness
- Weak muscles
- Tremors
- Irregular/fast heartbeat
- Increased volumes of sweat
- diarrhoea
- Loss of weight
- Protruding/bulging eyes
- Tenderness/swelling in the neck area
- Poor tolerance to exercise
- Irregular menstrual periods
Thyroid Nodules and Thyroid Cancer
Small lumps can form in the thyroid, either as cysts or solid masses, known as thyroid nodules. These lumps are most often benign, although in some instances they may be malignant, and an indication of thyroid cancer. This type of thyroid condition often is accompanied by no symptoms, but some may experience:
- Enlarged/swollen thyroid
- Voice change (as the thyroid is situated near the larynx, or voice box as it is commonly known)
Overactive Parathyroid Glands
This type of condition is highly rare in children, a parathyroid problem is when one or more glands are overactive. This can lead to high levels of calcium within the blood, as well as:
- Weakness
- Tiredness
- Headache
- Constipation
- Kidney stones
Causes of Thyroid Problems in Children
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism can be caused by numerous conditions, including:
- Grave’s disease – Overproduction of thyroid hormone.
- Toxic adenomas – The formulation of nodules within the thyroid gland which release thyroid hormones.
- Subacute thyroiditis – Where the thyroid gland becomes inflamed and leaks excessive amounts of hormones.
- Malfunction of the pituitary glands/thyroid gland cancer – Although uncommon, cancer of the thyroid gland can cause hyperthyroidism.
Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism can be caused by numerous conditions, including:
- Hashimoto’s thyroiditis – Where the body attacks the tissue of the thyroid, which eventually causes the tissue to die and halt the performance of hormones.
- Thyroid gland removal – Where the gland is either surgically or chemically removed/destroyed.
- Too much iodine – Some medication and medical practices may expose individuals to too much iodine, which can lead to the development of hypothyroidism.
- Lithium has been known to lead to hypothyroidism when consumed.
Thyroid Nodules
- Iodine deficiency – Much like too much iodine can cause health implications, too little within your diet can lead to the production of nodules in your thyroid. Due to the fact that iodine is often added to numerous food products, including table salt, iodine deficiencies are rare in the United States.
- Overgrowth of normal thyroid tissue – It is still unknown how or why this condition, also known as thyroid adenoma, develops. The growths are not a serious problem as they are benign, and only cause an issue when their size becomes bothersome.
- Thyroid cyst – When adenomas begin to degenerate, they often form cysts. Cysts are cavities that are filled with fluid, and are most often benign, but can sometimes be malignant.
Treatments for Thyroid Problems in Children
Hypothyroidism
This condition is almost always treated with daily medicinal pills to overcome the deficiency of thyroid hormones, which often lasts a lifetime. The treatment is only discontinued when the thyroid begins to function normally.
Hyperthyroidism
This condition is often treated in the following ways:
- Medication to slow or prevent thyroid hormone production (often only temporary).
- Thyroid ablation – Destroying the gland via consumption of iodine based radioactive drink.
- Surgery may be performed to remove the hormone producing thyroid gland.
Note: The treatments noted above may lead to hypothyroidism.
Thyroid Nodules
This condition is first determined via a physical exam; if further testing is needed, an ultra-scan is often applied. Surgery is often the best cause of treatment for this condition.
Thyroid Cancer
If a biopsy is performed and this condition is confirmed, surgery is usually the best option to remove the growth. Followup treatments of radioactive iodine may also be used to remove any further thyroid tissue. This treatment will generally require patients to take a thyroid pill indefinitely, on a daily basis.
