Ultrasound examination allows doctors and healthcare professionals to learn about the diseases and disorders. Specific prerequisites are not required for every ultrasound examination, but some tests definitely require preparation such as emptying stomach or filling the bladder. The total abdominal ultrasound is used to find abnormalities in the gallbladder, pancreas, liver, aorta, spleen and kidneys.Routine images are also taken to measure the dimensions of these organs and to observe focal abnormalities, if any. There are certain factors which are essential for abdominal ultrasound preparation.
What Is Abdominal Ultrasound?
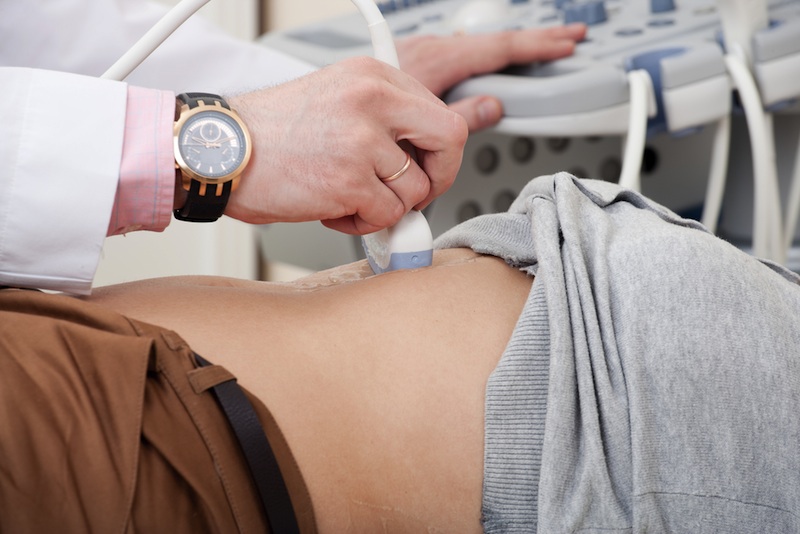 Abdominal ultrasound is done by using reflected waves of sound to make images of stomach (abdomen) and other internal organs. The examination for ultrasound is performed by a sonographer. He places a transducer—a small sized device that looks like microphone—on the examination area and electronically records the images. These images taken in ultrasound show inside organs and the flow of blood towards them. X-rays and other kinds or radiations are not used in the ultrasound.
Abdominal ultrasound is done by using reflected waves of sound to make images of stomach (abdomen) and other internal organs. The examination for ultrasound is performed by a sonographer. He places a transducer—a small sized device that looks like microphone—on the examination area and electronically records the images. These images taken in ultrasound show inside organs and the flow of blood towards them. X-rays and other kinds or radiations are not used in the ultrasound.
Essential Abdominal Ultrasound Preparations
If you have undergone upper gastrointestinal (GI) test or barium enema in the previous 2 days, notify your doctor. Otherwise the result of ultrasound can get affected due to the presence of barium inside your intestines. Some other tips for abdominal ultrasound prep prepared are discussed as under:
- If you are going for the ultrasound of your gallbladder, liver, pancreas and spleen then you will be told to have a no-fat meal an evening before the test. For this ultrasound, the stomach must be empty so you will be asked not to eat anything 8-12 hours before the examination.
- If you are going to get your kidneys examined, then you will be told to drink water or any liquid around 4-6 glasses an hour before the examination so that your bladder is completely filled during the test. You may also be told not to eat anything for 8-12 hours before the process so that there is no build-up of gas in intestines to ensure better visualization.
- In case if you are getting your aorta examined, you will be asked not to eat for around 8-12 hours before the scheduled examination time.
What to Expect During Abdominal Ultrasound
 There is no pain while imaging process of ultrasound, it is easy and fast. The total time of examination is 30 minutes and you have to change into gown for it.
There is no pain while imaging process of ultrasound, it is easy and fast. The total time of examination is 30 minutes and you have to change into gown for it.
Step 1: You will need to position on a smooth table on your back in the Department of Radiology, and a pillow can be given for your comfort.
Step 2: Gentle warmth is applied by a sonographer at first, and then your technician will apply a clear gel on the abdomen so that the transducer can be contacted directly with the skin.
Step 3: The transducer is placed against your skin firmly by the sonographer and moved back and forth to capture the images of abdomen.By the movement of transducer over abdomen, the pressure and mild discomfort can be felt, which will be greater if you're already experiencing pain in the abdomen.
Step 4: When the test is done, the images are reviewed by the sonographer with radiologist.
When to Employ Abdominal Ultrasound
Abdominal ultrasound is employed for various reasons. With proper abdominal ultrasound prep, you can learn the following from the examination:
- To know the reason behind your belly pain.
- To detect, measure and read the aneurysm present in your aorta. An aneurysm can result in producing a huge, pulsing lump in belly.
- Read size, position and shape of liver along with the problems inside, including jaundice, fatty liver or cirrhosis. It can also be used as a follow-up test after the liver function examination.
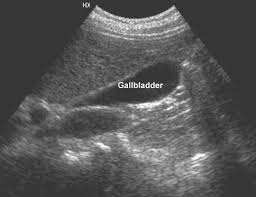
- It notifies inflammation and gallstones in bladder and also possible blocked bile ducts.
- Measure the enlarged spleen size and find the disease or damage that may have been caused.
- Look for problems in pancreas, like tumor.
- Check the blocked flow of urine in kidney. Ultrasound of kidney can also find the kidney size if needed and detects the mass and fluids around them. It is also used to find the reasons of infection in bladder. It is also used to follow-up after the kidney transplant.
- To find if the mass inside the belly is a cyst filled with fluid or a solid tumor.
- To guide the needle placement and other tools to be used during biopsy.
- Check if there is fluid developed in your belly cavity, if there is then the problem is known as ascites. Ultrasound can also be done during paracentesis to guide the needle placement to remove fluid from cavity of belly.
How About the Results of Abdominal Ultrasound?
Abdominal ultrasound prep plays a vital role in establishing accurate diagnosis and taking vital decisions for treatment. The ultrasound images are usually used to determine the results and the doctor checks if you have abdominal aortic aneurysm. If there are any signs found, the doctor recommends these choices:
1. Normal Results
It more than better to see the normal results after the cautious abdominal ultrasound prep. For normal results, you can expect:
- Organs are showed to be normal, including shape, size and texture, with no fluid or growths being seen.
- No kidney stones are showed and the drainage system of kidney function smooth without being blocked.
- Aorta is tested to be normal with no aneurysms being showed.
- The bile duct is in normal size. The gallbladder wall is showed with proper thickness with no gallstone being showed.
2. Suggest Waiting
If the aneurysm diameter is relatively smaller in size (less than 2 inches), your aneurysm isn't serious enough to require surgery. The doctor will then monitor and check the condition with the help of subsequent ultrasound tests and other imaging exams every 6-12 months.
3. Open Aneurysm Repair
If the aneurysm is very serious and requires surgery, doctor suggests open aneurysm repair. In such a procedure, the abdomen is opened in the process and the portion of abdominal aorta having aneurysm is removed and replaced with tube like graft.
4. EndovascularStent Graft
This procedure is less invasive. It enforces the weak part of abdominal aorta using the graft just like the type which was used in open aneurysm repair.A synthetic graft is attached at the catheter's end through an artery present in leg and threaded up into aorta. The graft is placed at aneurysm site and fastened using small pins and hooks. It later supports weak part of aorta and prevents rupture.
NOTE: Open surgery takes more time to recover than the endovascular one but endovascular surgery has more follow-up appointments. Survival rates of both kinds of surgeries are identical.
