Epidural block with anesthetics is the most common medication given in labor and delivery. This medication is injected into the ‘epidural space’, within the back to block the pain from labor by deadening the nerves that carry the pain signals to the brain. The medication is first given in a small dose to see if any adverse reactions become apparent, if not, the full dose is given. Epidural pros and cons are listed here to help you make the decision.
Pros of Having an Epidural
1. Reduce Labor Pain
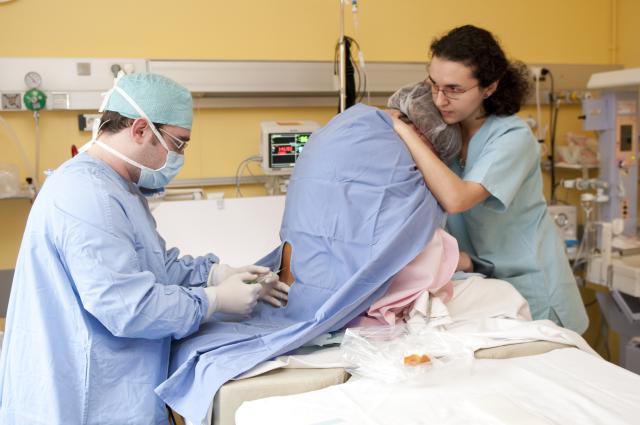 The most obvious positive point to having an epidural is that is will ease the pain experienced during labor, all the while having no effect on the birthing mothers’ cognitive state or ability. As mentioned, giving birth can be extremely painful, making this medication extremely useful at relieving pain for extended periods of time.
The most obvious positive point to having an epidural is that is will ease the pain experienced during labor, all the while having no effect on the birthing mothers’ cognitive state or ability. As mentioned, giving birth can be extremely painful, making this medication extremely useful at relieving pain for extended periods of time.
2. Relieve Anxiety
If the mother is anxious during labor, which is a natural state of being during such an occasion, contractions and labor can be slowed, due to the production of hormones related to stress (epinephrine and norepinephrine), a result of anxiety. An epidural will allow the mother to be relieved from pain, giving them the opportunity to rest and relieve some of their anxious thoughts. An epidural will also help to lower blood pressure, which can be beneficial to birthing mothers who have labor related hypertension.
3. Keep the Mother Alert
When trying to understand epidural pros and cons during labor, it is important to consider the different ways in which children are delivered. An epidural can be extremely beneficial to mothers who are giving birth via the cesarean method, as it will allow them to remain relatively free from pain, whilst continuing to be alert and active, so as not to miss the magical moment. It also means that there is no need for general anesthesia, which is thought to pose a greater risk than an epidural.
4. Muscle Function Normal
Epidural medication works to relieve pain without interfering with other muscle functions or bodily sensations, meaning that the mother will still have full control over her body, and full awareness of the situation.
Cons of Having an Epidural
1. Negative Effects on the Birthing Mother
- Inadvertent spinal block that can lead to severe spinal headaches which require numerous days of bed rest.
- Shivering (this can be reduced by lowering the dose of medication given; by warming the medication before administering it; or by mixing the medication with other narcotics.
- If narcotics are added, this can cause itching of the skin (mild or severe)
- Urine retention
2. Negative Effects on Labor
- Within this article of epidural pros and cons, it was stated that the medication can help to speed up labor by reducing a mother’s anxiety. The opposite is also true, as administration of this medication can also slow labor on some occasions, and it is also to increase the chances of requiring a cesarean birth by up to three times.
- The medication can slow the second stage of pregnancy by lessening or removing the natural stream of oxytocin. In many cases of epidural use, vacuum extractors or forceps are more likely necessary during labor.
3. Negative Effect on the Fetus
- Use of epidural may lead the fetus to develop an irregular heartbeat, requiring an oxygen mask for the mother and possibly the need for a cesarean birth.
- This medication may lead the mother to experience what is known as an ‘epidural fever’, which can lead to fetal tachycardia in the fetus, or newborn fever. This will require the newborn to undergo more medication and isolation whilst the condition is healed.
- The medication may become confined within fetal circulation, which can lead to more prominent effects on the newborn (listed below).
4. Negative Effects on the Newborn Baby
- Short term effects on the new born baby resulting from epidural use include inconsolability, irritability, decreased ability at shitting out noise and light, and decreased ability to visually track objects. There is little to no data regarding long term effects on new born babies resulting from epidural use.
- It is possible that you will notice increased difficulty in feeding the newborn due to the effect the epidural can have on normal suckling and rooting behavior.
- It may also lead to decreased responsiveness from the new born, which can have a lasting effect on the bond between parent and child.
Other Pain Medications Used in Labor and Delivery
Now that epidural pros and cons have been laid out for you, you can make an informed decision on whether to use the medication or not. It is important to remember that other medications are available to help relive the pain experienced during labor, most of which are listed below:
1. Spinal Block
Description: This medication is very similar to an epidural, and it is often administered before carrying cesarean. The medication is administered the same way as an epidural, and the two medications are often used together.
Pros: Provides a good amount of pain relief for extended periods of time, only requiring one small dose to have a beneficial effect. The mother will remain alert, and the medication often has little to no effect on the fetus.
Cons: The medication can work to reduce blood pressure, which in turn can lead to a slowing of the baby’s heart rate. It can also lead to a momentary occurrence of breathing difficulties, if the medication affects the chest wall. Urine retention is also possible as a result of this medication, as well as severe headaches.
2. Narcotics
Description: There are numerous narcotics, or opioids, that can be administered during labor to help ease pain and discomfort.
Pros: The medication will work to decrease one’s perception of pain for an extended period of time (up to six hours).
Cons: The medication does not actually reduce pain. It is also possible that the medication may cause nausea and sleepiness for the mother, and reduce breathing for the mother or the baby.
3. Local Anesthetic Injection
Description: This medication doesn’t work to relieve pain, but it is helpful in numbing the vaginal area, if an episiotomy is required.
Pros: The medication numbs the desired area, and it is rare for there to be a negative effect on the mother or the baby.
Cons: The medication, as mentioned, does not relieve pain. It is also possible for the mother to have an allergic reaction. In rare cases, it may also lead to a decrease in blood pressure.
4. Pudendal Block
Description: This medication can be administered just before the baby is born, and it works to block the pain between the vagina and the anus (called the perineum). Local anesthetic is administered into the vaginal wall, which takes effect shortly after around ten to twenty minutes.
Pros: The medication works to relieve pain, and negative side effects are rare.
Cons: It is possible that the medication will be ineffective, or only work on once side of the perineum. An allergic reaction is possible, and an infection can occur at the sit of administration. It may also lower blood pressure if injected into a vein.
5. Tranquilizers
Description: Although this medication is rarely used, it can be administered to reduce anxiety and help the birthing mother to rest and relax. This can be injected or administered via an IV.
Pros: The medication helps to relieve anxiety as well as help to increase the possibility of relaxation.
Cons: The medication does not eradicate pain. It may also lead to drowsiness, and an inability to remember your labor. The baby may also be affected, causing a decrease in their activity and muscle tone once born.
6. Nitrous Oxide
Description: This medication is often inhaled during labor via the use of a hand held mask in places like Canada and the UK, although it is rarely used in the USA.
Pros: The medication can help to reduce one’s perception of pain. The mother also has full control over administration, if they begin to feel drowsy, they can simply stop breathing through the hand held mask. The medication also has little to no effect on the fetus/newborn.
Cons: The medication does not eradicate pain, and can also lead to nausea and dizziness.
