The top part of the femur consists of a ball, which fits in to the ball and socket hip joint. A femoral neck fracture is caused when the ball of the bone is fractured off. When this fracture occurs, the blood supply to the bone is disrupted and this can cause delay in healing or not healing of the fracture. Depending on the severity of the fracture and the age of the patient, the treatment will be carried out. If the ball of the bone is out of the normal position, the treatment will differ. Usually these fractures are treated by a partial hip replacement surgery, owing to the hindered blood supply.
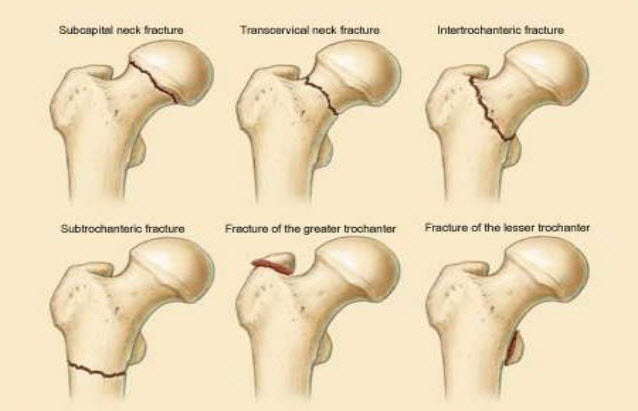
Presentation of Femoral Neck Fracture
The fracture can be either impacted/stress facture or a displaced fracture. Symptoms of a stress fracture are – pain in the groin, referred pain in the thigh and knees, along the median. For a displaced fracture, there is pain in the entire hip region.
A physical examination of stress fracture involves checking for any obvious clinical deformity, discomfort when there is movement in the hip, either active or passive. When there is extreme motion, it can cause muscular spasms. There is pain in the greater trochanter with percussion.
For displaced fracture, it involves moving the leg in abduction and external rotation.
What Causes Femoral Neck Fracture?
The most common cause of femoral neck fracture is when elderly people fall, or accidents or trauma caused in younger people.
When elderly people fall the mechanism can either be direct impact on the hip when falling or a twist, where the foot remains in the same position and the body rotates. The fractured bone is deficient in elastic resistance. Elderly people are at higher risk because of osteoporosis and osteomalacia. Also women are more prone because of higher occurrence of osteoporosis, which makes the bones weak and fragile.
In a trauma involving younger people, there is axial load along with high force. The fracture of neck femor is caused due to an abducted hip, or it can also lead to hip fracture dislocation.
Complications
There can be a lot of blood loss in closed fractures, which might not be obvious till there is swelling in the thighs.
Further complications, which could arise, are deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, fat embolism, infection, angulation, nonunion and shortening.
Treatments for Femoral Neck Fracture
Medication
The main concern of medication in femoral neck fracture is pain management. The acute pain experienced in fracture is addressed by administering acetaminophen or NSAID. If these medicines do not work or give pain relief, then additional medication might be required. For such cases, opiates are given, which will provide relief from breakthrough pain. In acute phase, pain medication will have to be adjusted frequently.
Surgical Intervention
For surgery, the most important criteria are the age of the patient and the amount of displacement caused by the fracture. When the age of the patient is less than 60 years, partial hip replacement is avoided as much as possible as it will wear out faster in more active younger patients.
Hip Pinning
Hip pinning involves placing screws along the fractured bone. This procedure is done when there is minimal displacement and is well aligned. To avoid hip replacement in younger patients, it is done even when there is improper alignment.
The procedure is carried out under spinal or general anesthesia. Small incision in the thigh is done and with help of x-ray the surgeon places the screws, which stabilize the bone.
Depending on the tolerance level, weight can be put on the hips. The pain will subside when bones heal. If there is non-healing or bone death due to loss of blood supply, hip replacement might be required.
Hip Hemiarthroplasty
This term means half of hip replacement, where only the ball of the bone is removed and replaced with metal prosthesis. Since there can be complications in repairing the fracture, especially involving displacement, this technique is preferred.
This surgery is also performed under spinal or general anesthesia. With an incision outside the hip, the fractured portion of the femoral head is removed.
Rehabilitation of such patients is initiated as the earliest and walking commenced with full weight on the implant.
Physical Therapy During Recovery
Physical therapy forms part of the rehabilitation program and includes different types of activities. Some of them are given below:
Running:
The introduction to running is slow and the distance is also gradually increased. If there is pain, a break of few days is taken. Depending on the symptoms, the mileage is gradually increased and progressed.
Strengthening:
This deals with strengthening of a hip abductor muscle – gluteus medius along with other muscles of the region. It helps in improving and normalizing the gait, after which sport specific training is done.
Aerobic Exercise:
It is essential to have aerobic exercises done during the rehabilitation program. For non-weight bearing ambulation, upper body exercises can be done. After that swimming or deep-water running can be included in the regime.
