Nosebleeds are quite common but they can still be quite scary. You do not need to worry too much because they rarely indicate any serious underlying medical condition. There are many blood vessels in the back and front of the nose, and they can bleed easily with little irritation. Children between 3-10 years old and adults are very common to have nosebleeds. Some people get it more often, and this makes them ask, "Why do I keep getting bloody noses?" Let's find out the answer.
Causes of Blood Noses

Nosebleeds can be of two different types. It may be an anterior nosebleed, which means the blood vessels in the front of your nose have broken. It may also be a posterior nosebleed, which means the bleeding started in the deepest part of your nose. In a posterior nosebleed, some blood may also flow back to your throat, which makes this type of bleeding rather dangerous.
Many things can cause nosebleeds. You do not usually need to worry about a sudden nosebleed, but there may be an underlying issue if you have frequent nosebleeds. Here are some of the common answers to "Why do I keep getting bloody noses?"
1. Dry Air or Irritating Fumes
Those who live in a dry climate are more likely to experience bloody noses. This happens when the lining of the nose becomes very dry, which in turn makes it easier for blood vessels to break and bleed. You may also get frequent nosebleeds if you are exposed to toxic fumes which can irritate the lining of the nose.
2. Nose Scratching
You increase your risk of experiencing nosebleeds by picking your nose too often. Scratching inside your nose may damage the blood vessels in the nostril and cause a nosebleed.
3. Blood-Thinning Medications
Taking blood-thinning medications such as aspirin as well as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS) increases your risk of having nosebleeds. These medications affect your body's ability to clot. Therefore, if you are taking anticoagulants, anti-platelet medications, or OTC drugs like aspirin, you may get nosebleeds frequently.
4. Underlying Health Conditions
Nosebleeds can be a symptom of underlying health conditions, such as kidney disease and liver disease. Certain heart conditions such as congestive heart failure and hypertension can also cause nosebleeds. What's more, allergies and colds can irritate the lining of your nose and cause nosebleeds.
5. Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia (HHT)
Also known as Osler-Weber-Rendu syndrome, HHT is a genetic disorder affecting both males and females of all racial and ethnic groups. You may experience frequent nosebleeds when you have HHT because it causes abnormal blood vessels to bleed easily. The abnormality may also affect other organs and systems including the brain, lungs, and digestive system.
5. Deviated Septum
The cartilage and bone that divide the nasal cavity in half is called the nasal septum, and a deviated septum means it is crooked or off center. This deformity will make breathing difficult. Someone with a deviated septum will experience nasal congestion with one side being more congested. Other symptoms include facial pain, frequent nosebleeds, postnasal drip, and headache.
6. Drug Abuse
Why do I keep getting bloody noses? People who use drugs often ask this. The condition is more common in people who snort drugs like cocaine. The substance they snort irritates the nasal membrane and damages blood vessels, resulting in nose bleeding.
7. Other Causes
- The air is thinner and drier at a high altitude, which can result in nose bleeding.
- Nasal tumors and vascular malformations in the nose
- Overuse of nasal decongestants
- Sinusitis, the infection of cavities inside your forehead and cheekbone
- Von Willebrand disease, haemophilia, or other blood clotting abnormality
- Nasal surgery
- Hormonal changes during pregnancy
- Hardened arteries
When to See a Doctor
Since most nosebleeds are not that serious, you do not usually need any treatment. You should see your doctor if:
- Your bleeding does not stop even after punching your nose for 10 minutes
- You experience nosebleeds regularly
- You feel lightheaded and dizzy when your nose bleeds
- Your heart rate elevates and you have trouble breathing
- You cough up blood
- You have a fever greater than 38.5 °C
If you experience any of these symptoms, you should seek immediate medical attention. Do not drive when you are experiencing the symptoms. Ask someone to drive you or call your local emergency number for help.
How to Stop a Bloody Nose
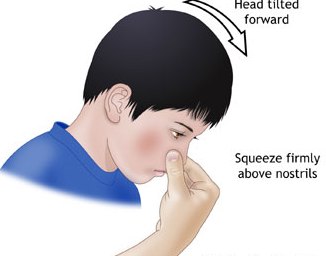
Here are the steps to follow to stop a bloody nose without the help of a healthcare professional.
- Pinch your nose. You should be pinching all the soft parts together with the help of your index finger and thumb.
- Pinch and press toward your face or against the bones of the face.
- Lean forward slightly while pinching your nose to avoid sending the blood back into the throat and sinuses.
- Hold the same position for at least five minutes and repeat if necessary.
- Maintain an upright posture once the bleeding has stopped and never put your head below the level of the heart.
- Wrap an ice cube in a cloth and apply it to your cheeks and nose for quick relief.
How to Prevent a Bloody Nose
Why do I keep getting bloody noses and how to prevent it? You are more likely to experience nosebleeds in cold, dry climates. Using a humidifier may resolve the issue. Similarly, using an OTC nasal lubricant spray, petroleum jelly, or a saline nasal spray may help keep your nose moist. Here are some other tips to help prevent bloody noses.
- Do not blow your nose with force and avoid picking your nose.
- Do not smoke as it contributes to nasal irritation and dryness.
- Follow your doctor's advice when taking blood-thinning medications such as aspirin.
- Do not overuse decongestants and antihistamines to prevent nasal dryness.
Talk to your doctor if your nosebleed is due to another medical condition such as nasal allergies, liver disease, or a chronic sinus condition. Follow your doctor's advice to keep things under control.
