Finding a breast lump can be terrifying. Breast lumps are noticeably separate from the normal tissue in your breast area. They affect both men and women, but happen more often in women. While not all lumps in the breast are related to breast cancer, some could be. There are many different causes of breast lump like fibrocystic breasts, mastitis (infection), fibroadenoma, and breast trauma. Any breast lumps need to be checked by your doctor.
What does Movable Lump in Breast Indicate?
Most causes of movable breast lump are benign (non-cancerous), however any breast lump needs to be evaluated by your doctor just to rule out any underlying conditions. Below are some of the causes:
1. Premenstrual Breast Tissue Changes

Some women experience breast tissue changes in the weeks before a period. They tend to disappear after your period is over. They are caused by your hormones going up prior to your period.
Symptoms include very large lumps of hard tissue that move around, tender sore breasts, swelling, and discomfort when wearing a bra. The levels of estrogen rise and your milk ducts begin to grow. Your progesterone then rises and causes swelling in your milk glands. You may even be feeling the swollen milk ducts.
Premenstrual breast tissue changes are usually nothing to worry about. If you develop a lump or lumps that do not go away with your period, then you should contact your doctor.
Cancer Risk: Benign
2. Fibrocystic Breast Disease
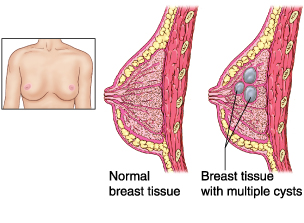
If you have painful lumps in your breast or breasts over most of the month, you may have fibrocystic breast disease. This is a benign condition that also flares according to hormonal changes. When your ovaries produce hormones, your breast tissue may respond by becoming thick and lumpy. Symptoms include lump or lumps in the breast, band of hard breast tissue, pain in the area of the lumps, and breast soreness.
This condition is most common in women 30 to 50 years old and can be painful. It is estimated that over half of all women experience this disease. It doesn't lead to breast cancer, but doctors may have a hard time telling fibrocystic disease from cancerous lesions.
Cancer Risk: Benign, but can mask cancerous lesions in the breast.
3. Fatty Tumors (Lipoma)
 If you find a movable lump in breast that is actually quite large, it may be a lipoma. These are fatty deposits just under your skin. Lipomas are benign tumors that grow very slowly, so you may not have even noticed them when they were small. These don't turn into cancer or cause cancer, but can grow large enough to cause you some issues. It is a good idea to have them checked out and they can be removed if necessary.
If you find a movable lump in breast that is actually quite large, it may be a lipoma. These are fatty deposits just under your skin. Lipomas are benign tumors that grow very slowly, so you may not have even noticed them when they were small. These don't turn into cancer or cause cancer, but can grow large enough to cause you some issues. It is a good idea to have them checked out and they can be removed if necessary.
Cancer Risk: Benign
4. Fibroadenoma
A fibroadenoma is a tumor that is made up of connective and breast tissue. Around 10 percent of women in the US have fibroadenomas and they are benign. If you take oral birth control pills before 20 years old, it can put you at a high risk for these tumors. They are also more common in pregnancy, and usually go away after menopause.
Symptoms include small lump that is very different from other breast tissue, lump is movable, not painful, and it feels like hard rubber.
Cancer Risk: Increased Risk. There is a small increased risk of breast cancer with fibroadenoma. Doctors suggest regular self-breast exams, mammograms, and routine exams.
5. Mastitis
When you get a breast infection, it is known as mastitis. It can cause a lump or abscess with redness and swelling. It can happen to new moms who are breastfeeding, or anyone who gets a plugged milk duct. The actual plugged duct can cause a movable lump in breast and needs to be treated with antibiotics as soon as possible.
Symptoms also include breast swelling, redness, tenderness, fever, and warmth of the skin.
Cancer Risk: Benign. While mastitis does not put you at risk for cancer, it may actually be inflammatory breast cancer and not mastitis. This is usually found when treatment with antibiotics does not improve the condition.
6. Gynecomastia
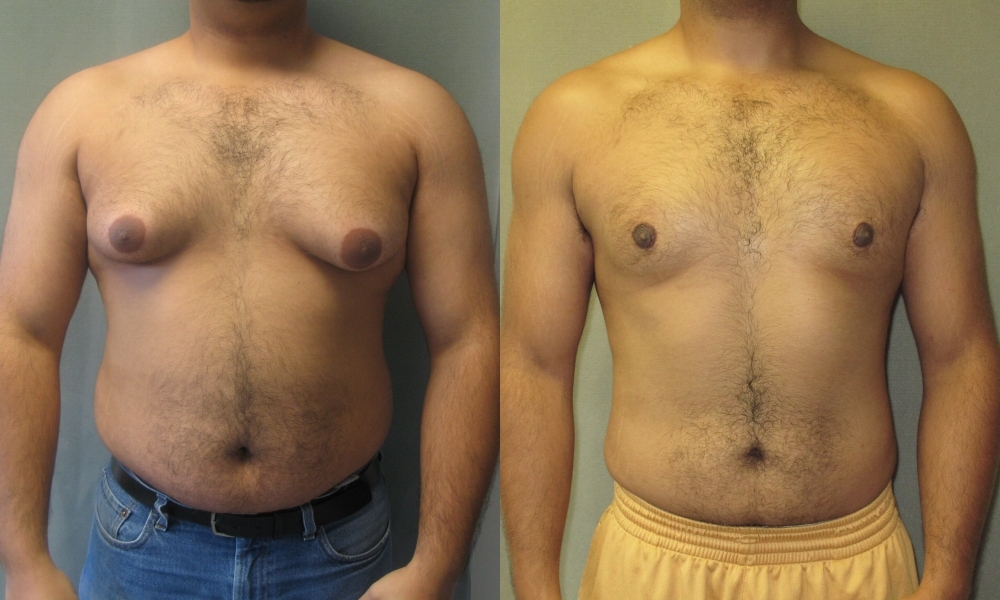 This is a condition where firm breast tissue grows in males and the breasts become enlarged. It is usually due to hormonal changes or certain medications. Men can develop a lump in their breast and be concerned about breast cancer. Yes, men can get breast cancer but it is very rare. Gynecomastia is most often a benign condition and reverses once the hormones stabilize.
This is a condition where firm breast tissue grows in males and the breasts become enlarged. It is usually due to hormonal changes or certain medications. Men can develop a lump in their breast and be concerned about breast cancer. Yes, men can get breast cancer but it is very rare. Gynecomastia is most often a benign condition and reverses once the hormones stabilize.
Symptoms include enlarged breasts in males, lumps near or under the nipple, and sometimes breast tenderness.
Cancer Risk: Benign
7. Intraductal Papilloma
This small movable lump in breast is actually a benign tumor in one of your milk ducts. It's most often felt near or around your nipple. It's a benign tumor and most often appears in women between 35 and 55 years of age.
Symptoms include small movable lumps near the nipple, nipple discharge, and pain in some cases. The lumps measure around 1 to 2 centimeters and can appear in clusters around the nipple.
Cancer Risk: Benign, but if you develop an unusual amount of these you can be at an increased risk for breast cancer. Your doctor may want to do a biopsy on these lesions and keep a close eye on them.
8. Breast Cancer
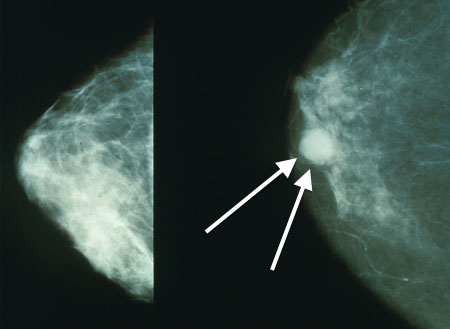 Breast cancer is an abnormal overgrowth of cells in the breast tissue. It causes a lump that grows larger and more painful, sometimes quickly. It affects mostly women, but men can get breast cancer too.
Breast cancer is an abnormal overgrowth of cells in the breast tissue. It causes a lump that grows larger and more painful, sometimes quickly. It affects mostly women, but men can get breast cancer too.
Symptoms include breast lump, pain, tenderness, and redness. Lump grows over a short amount of time. The lesion may even break through the skin and form an open sore.
Cancer Risk: Malignant/Cancerous, but treatable if caught early.
