Staphylococcus aureus is one of the most important disease-causing
bacteria known to man. It damages your skin and soft tissues and leads to issues like furuncles, abscesses, and cellulitis. It is worth mentioning that most staph infections aren't that serious, but Staphylococcus aureus can easily make things difficult by causing serious infections such as pneumonia, bloodstream infections, and bone/joint infections. It is important to learn more about this bacterium and learn how to treat different infections it can cause. Keep reading to find out more.
What Is Staphylococcus Aureus?
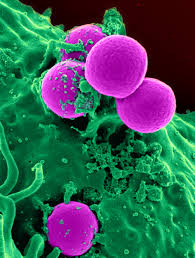 First identified by the surgeon Sir Alexander Ogston in 1880, it is coccal bacterium that belongs to the Firmicutes family and lives on your skin or in your respiratory tract. It is usually positive for catalase and nitrate reduction. It is not always pathogenic; in fact, studies show that about 20% of humans are long-term carriers of this bacterium – it lives as part of the normal skin flora.
First identified by the surgeon Sir Alexander Ogston in 1880, it is coccal bacterium that belongs to the Firmicutes family and lives on your skin or in your respiratory tract. It is usually positive for catalase and nitrate reduction. It is not always pathogenic; in fact, studies show that about 20% of humans are long-term carriers of this bacterium – it lives as part of the normal skin flora.
It is sometimes the underlying cause of skin infections, respiratory infections such as sinusitis, abscesses, and food poisoning. It can cause many other types of skin infections including boils, impetigo, pimples, scalded skin syndrome, carbuncles, and folliculitis. It is also responsible for several life-threatening infections such as meningitis, toxic shock syndrome, osteomyelitis, sepsis, and endocarditis. It is responsible for sending about 500,000 people in the U.S. to hospitals each year.
Symptoms of Staphylococcus aureus Infection
Staph infections aren't that serious in most cases, but Staphylococcus aureus can cause several life-threatening complications, including the infection of the inner lining of your heart. However, the signs and symptoms of staph infections vary greatly, the majority of which are listed as below:
1. Skin Infections
It can cause different types of skin diseases, so symptoms may vary in different cases.
- Boils: If you're dealing with boils, it usually means you're infected with Staphylococcus aureus. You will also notice your skin around the boil become red and swollen.
- Impetigo: Staph bacteria can also cause a painful rash, which is another common symptom of staph infection. Impetigo will cause large blisters with fluid and crust.
- Cellulitis: It refers to the infection of the deeper skin and also causes swelling and redness on the surface of your skin. Sores may also develop in some cases. It usually affects the feet and lower legs.
- Staphylococcal Scalded Skin Syndrome: Staph infection will lead to the production of toxins that cause this syndrome, which usually affects children and newborns. It features a rash, fever, and blisters.
2. Food Poisoning
The reason behind your food poisoning could be staph bacteria. You may notice several symptoms that may develop quickly – they usually disappear quickly too. You don’t usually get any fever but you may have to deal with diarrhea, low blood pressure, dehydration, nausea and vomiting.
3. Bacteremia
It refers to blood poisoning and occurs when Staphylococcus aureus or staph bacteria enter your bloodstream. The most common signs are a fever and low blood pressure, but you may notice some other symptoms, such as infections affecting bones, muscles, cardiac pacemakers, artificial joints, and internal organs, including heart, brain, and lungs.
4. Toxic Shock Syndrome
Some strains of staph bacteria produce certain types of toxins that cause life-threatening conditions. It is usually associated with the skin wounds, surgery, and the use of specific tampons. It also produces several symptoms such as diarrhea, muscle aches, confusion, nausea, fever, and abdominal pain.
5. Septic Arthritis
Caused by staph infection, the condition affects the joints in your body, including your hip, ankle, knees, elbow, wrist, spine, and shoulder. Specific signs and symptoms include fever and severe pain in the joint with joint swelling.
Transmission of Staphylococcus aureus Infection
You can contract an infection either in the community or in hospitals. It spreads from person to person, usually from the hands of healthcare workers in hospitals. You may also become infected if you touch any object or surface already contaminated with Staphylococcus aureus. Skin scales from the body of an infected person may contaminate objects and surfaces. It can also spread by sharing personal items, such as towels, razors, washcloths, and soaps.
Treatments of Staphylococcus aureus Infection
There are a number of treatment options available to help clear any infection caused by Staphylococcus aureus. Here's more about treatments for your understanding:
1. Antibiotics
Like with all infections, the first treatment option involves taking some antibiotics. Antibiotics work but it is important to identify the type of staph bacteria causing trouble in your case. The most common antibiotics used for staph infections are nafcillin, cephalosporins, vancomycin, or sulfa drugs. Vancomycin is becoming an increasingly popular choice for doctors to treat staph infections because many of these bacteria have become resistant to other available medicines. It is important to complete your course of antibiotics even if you are feeling better after a few doses.
2. Wound Drainage
In case of a skin infection, your doctor will decide if it is important to drain it. For this, they will make an incision into the wound to drain fluid.
3. Device Removal
In case the infection is associated with a prosthetic or device, your doctor may consider removing it, which may need surgery.
Keep in mind that staph bacteria are very adaptable and soon become resistant to antibiotics. You should complete your course if your antibiotics are working. A good example of how adaptable these bacteria are is that only 10% of today's staph infections respond well to penicillin.
