Bruises can happen out of nowhere, but is almost always attributed to injury. They are broken blood vessels under the skin that appear black and blue. You can get a bruise from a few different things, including overuse of a body part during exercise, bleeding disorders, use of blood thinners, or a bump into something. A bruise should heal within a week to 10 days and if they don't, there may be something more going on.
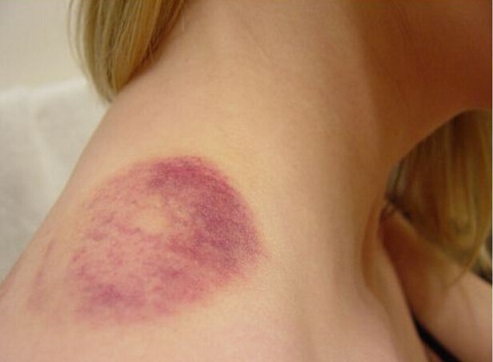
Reasons Why Your Bruises Won't Go Away
Bruises that won't go away are concerning and could indicate a variety of things, which include:
1. Nutrients Deficiency
If you are low on some nutrients, you may have issues with healing and blood clotting. This can be caused by deficiencies in:
- Vitamin C - This vitamin speeds up wound healing and keeps blood vessels healthy.
- Zinc - Zinc nourishes the skin and increases wound healing. Low zinc levels may also contribute to anemia and cause excessive bruising.
- Vitamin K - Vitamin K is needed by the body for proper blood clotting. People with vitamin K deficiencies may get more bruises with slower healing time.
- Bioflavonoids - These antioxidants help to nourish the skin and blood vessels. Eating enough foods with bioflavonoids may even help prevent bruising.
2. Hematoma
An injury that ruptures a blood vessel can cause bleeding that makes a huge lump. This is most common with a bump to the head, but can happen anywhere. While blood clotting usually closes up the rupture, people with bleeding issues or on blood thinning medications can have continuous bleeding. This will appear as a bruise over a lump in the skin area.
3. Advancing Age
As we get older, the ability to sustain bruises for any reason increases and the ability to heal decreases. This means we may bruise more easily as we age and the bruises may stay around longer than before. They fade very slowly, which are caused by the walls of the blood vessels weakening.
4. Heterotopic Ossification
This is a growth of bone into your soft tissues. In some cases, the friction of bone against the tissues may puncture a blood vessel and cause chronic bleeding and bruising. If this happens often, you may get bruises that won't go away.
5. Von Willebrand Disease
This is a blood clotting disorder where sufferers experience non-stop bleeding that can be very heavy. This is due to a low amount of a certain protein that helps blood clotting. Bruises can happen for little to no reason and persist for a long time.
6. Medications
Some medications can thin the blood too much and causes episodes of bleeding and bruising. You may notice bruises that stay long if you are on a daily dose of one of these medications. These include:
- Omega 3 Fatty Acids - This supplement can increase the risk of bleeding and bruising.
- Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRI's) - Some people have had increased bruising with these medications used for depression and anxiety.
- Blood Thinners - Warfarin, heparin, and low-dose baby aspirin. Long-term use of blood thinning medications can cause bruises that won't go away.
- Non-Steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDS) - Anti-inflammatory medications may also have blood thinning properties that increase the risk of internal bleeding.
7. Collagen Disorders
Disorders that occur due to a faulty collagen gene can cause blood vessels to rupture easily. One of these is called, Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome. Sufferers may notice bruises that seemingly come out of nowhere, even without a bump or injury. The bruises may heal slowly and occur often.
8. Hemophillia
This is a genetic disorder that causes people to have less clotting factor in the body. They are at risk for internal bleeding and bruising. People with hemophilla may require blood transfusions on a regular basis.
9. Thrombophilia
This condition is caused by low platelets in the blood and can raise the risk of bruising and bleeding. This is because the platelets do not form clots and stop bleeding. Because of this, bruises and bleeding can take longer to heal.
10. Chemotherapy
One of the side-effects of chemotherapy is reduced blood platelets that are essential in blood clotting. People undergoing chemo for cancer may notice an increased risk for bruising and bruises that won't go away as fast as they normally do.
What Can Be Done?
If a bruise is non-life threatening due to a chronic condition or serious injury, there are a few things you can do at home to help them heal faster. These include:
- Get enough vitamin C: Increasing your vitamin C intake may help the skin to heal from wounds and/or bruising faster. Just don't take more than 1,000 mg per day as too much can increase the risk of bleeding.
- Rest and ice: When you sustain a bruise, try staying off or not using that body part too much the first day. Rest and apply ice packs for 10 minutes on and then 20 minutes off, alternating. An easy and comfortable way to apply cold to a bruise or injury is to use frozen peas that will form to the body part. Always wrap ice packs in a towel to prevent frostbite.
- Vitamin K: Make sure you are getting enough vitamin K in your diet. This will help your blood to clot properly and heal bleeding and bruising issues faster. Foods that contain vitamin K include cabbage, broccoli, greens, prunes, and asparagus.
- Chocolate: Who doesn't love chocolate? Well, it has amazing health benefits too! The cocoa is naturally anti-inflammatory and can improve the health of your skin. Just melt some chocolate in the microwave or on the stove and smear onto the bruise. Cover with gauze and allow it to tighten blood vessels for bruises that won't go away.
- Sugar paste: Make a paste of sugar and a few drops of water. Place over the bruise and wrap with a bandage. Sit with an ice pack over the bandage, which helps keep the bruise from getting larger.
- Heat: You an alternate ice with hot packs to help relieve inflammation and increase blood flow to and away from the area. This helps speed up healing of bruises, by encouraging the body to go pick up old red blood cells and clear them from the body.
- Ace wrap: Try using a compression bandage to help stop bleeding under the skin. If you do this early on when you first notice a bruise, it may help it from becoming larger.
When to See a Doctor
Bruises show signs of healing when they do begin to spread, but turn lighter in color and yellow around the outer edges. If a bruise spreads, but remains purple or blue you should see a doctor as soon as possible. This could be a sign of actual internal bleeding which could be life threatening.
Also see a doctor if you sustain an unusual amount of bruises without any known cause or injury, or you repeatedly have bruises that won't go away.
