We use our hands for doing almost everything and any small, red bumps on hands are noticed immediately. There can be a lot of reasons for these bumps or redness, and most of these get better with time and are completely harmless. However, there are some serious medical conditions which can lead to formation of certain types of bumps. If there is no obvious reason like an insect bite or injury, and the bumps are not getting better, the best thing is to talk to your doctor.
Causes and Treatment of Small Red Bumps on Hands
1. Hand Eczema
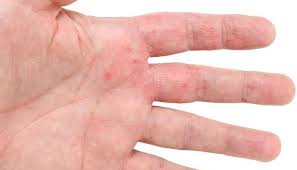
Eczema is a common skin problem and can affect children and grown-ups. It is known as atopic dermatitis and is characterized by a red, scaly and itchy rash. There can be swelling, oozing and crusting of the lesions. It can result from exposure to certain chemicals and the hands are very commonly involved.
Treatment:
Topical corticosteroids can be used to treat eczema or atopic dermatitis. The ideal way is to use them only when the rash flares up. Try to avoid exposure to irritants, and select soap or detergent which is free of irritant chemicals. Moisturize your hands after washing to keep the skin in good condition.
People who get it frequently are advised to wear gloves while handling chemicals, doing washing, or going outside in extreme weather.
2. Fungal Infection
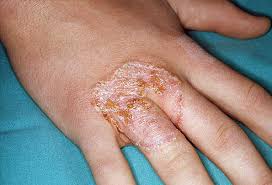
Fungal infection can result in formation of tiny bumps. Usually these small red bumps appear around the fingernails. People with diabetes and compromised immunity are more likely to develop fungal infections. These lesions caused by fungal infection are extremely itchy. Tiny blisters can develop with some crusting and scaling. If you have diabetes or any other underlying medical conditions, or these bumps are not getting better, seek medical advice and get treatment.
Treatment:
The fungal infection of skin is caused by various types of fungus and it is important to select the right anti-fungal medication for proper treatment. Your doctor can prescribe a cream or oral medicine depending upon the nature and severity of your infection. Many home remedies such as application of apple cider vinegar, yogurt and garlic are helpful.
3. Scabies
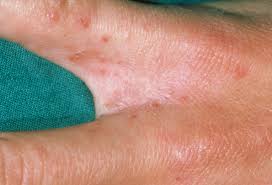
Scabies are tiny mites whose bites and burrows can cause formation of small red bumps on hands. The mites live and lay eggs in burrows. If you get infected, you may notice burrows which are small tracks under the skin, usually between the fingers. This condition is highly contagious and needs treatment.
Treatment:
The treatment for scabies is the application of anti-scabies lotion or creams. These contain 5% permethrin and benzyl benzoate. For itching, antihistamines and calamine lotion are very effective.
4. Dermatomyositis
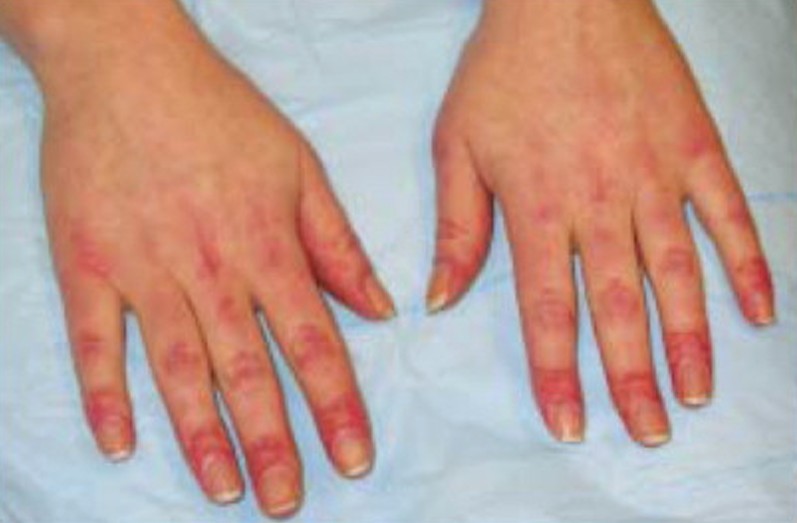
Dermatomyositis is a chronic disease of the muscles. A purple or red rash on finger joints or knuckles can be the first sign of it. This rash can appear on other parts of the body like face, back, knees, eyelids or shoulders and gets worse by exposure to light. Other symptoms include muscle weakness and inflammation.
Treatment:
There is no definitive treatment of dermatomyositis, but the severity of symptoms can be controlled by the use of corticosteroids, rituximab and some anti-malarial medicines. Physiotherapy is also very effective to regain muscle strength and flexibility.
5. Granuloma Annulare
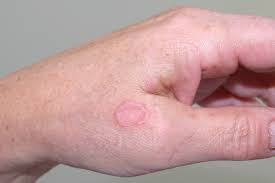
The exact cause of granuloma annulare is not known. This condition is characterized by formation of ring like lesions or bumps, especially on hands, elbows, knees or feet. These bumps can be of different colors. They can be skin colored, red, purple or whitish in color and are slightly itchy.
Treatment:
Most of these lesions disappear with time and do not need any treatment. If they are bothering you and you want to get treatment for cosmetic reasons, topical corticosteroids can be used. Light therapy and cryo-therapy (freezing) are also used to treat these lesions.
6. Rheumatoid Arthritis
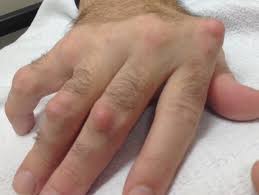
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease. In rheumatoid arthritis, the body produces antibodies against the joint lining, causing red bumps around the affected joints. Women are more likely to get this condition and the exact causes are not well known. Other symptoms include malaise, fatigue and fever.
Treatment:
There is no cure available for rheumatoid arthritis but disease modifying agents can control the symptoms effectively. The treatment of choice depends upon the severity of symptoms and many other factors, and can vary from person to person. Generally speaking, NSAIDs are often prescribed to control joint pains.
7. Folliculitis
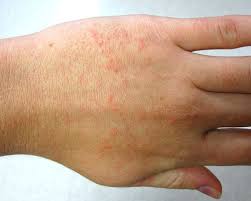
The inflammation of hair follicles or folliculitis is a very common skin disorder. It is caused by bacterial or fungal infection of the hair follicles, and it can cause small red bumps on hands if the hair follicles on hands are involved. They can also start as small pimples or ingrown hair. Some other symptoms are:
- Redness of skin
- Itching
- Formation of small pus-filled blisters which can burst
- Pain
- Swelling
Treatment:
Folliculitis gets better on its own within a couple of weeks if it is not very severe. For a speedy recovery you can:
- Use a hot compress. Soak a towel in hot water for a couple of minutes and then squeeze it to drain excess water. Wrap it over your hands and make sure that it is not too hot.
- Wash the affected area with medicated shampoo.
If the condition does not get better, talk to your doctor. He or she may prescribe oral or topical antibiotics.
8. Insect Bites
Insect bites like mosquito bites or bee stings can cause allergic reactions which cause small red bumps on hands. These tiny bumps are mostly noticed on the dorsal side of hands. You may also feel itchy and painful.
Treatment:
The pain and itching caused by insect bites don't need any specific treatment if these symptoms are mild. If the itching or pain is severe, antihistamines and painkillers can be taken. Local application of anesthetic creams and topical corticosteroids is also effective to control the pain and swelling.
Things You Should Remember
- These red bumps on hands can be itchy, but try to control the urge to scratch. This can irritate the skin and can delay the healing process. Never squeeze or pop them as it can lead to scarring.
- Avoid soaps and detergents containing harsh chemicals. Use mild soaps which do not irritate the skin.
- Avoid staying in sun for longer times, and keep yourself well hydrated. This will protect your skin and make it less prone to infection and inflammation.
- You can use petroleum jelly to keep your skin well moisturized.
