Looking for an antibiotic to treat folliculitis? Folliculitis causes itching and tiny red bumps near where the hair grows that signals an infected hair follicle. When the hair follicle becomes infected, it could either be a fungal or a bacterial infection. While the condition isn't too serious, an untreated infection can leave you with permanent damage to the hair follicle. Most cases clear on their own in a few days, but if it doesn't clear up, you need to see your doctor. This article explains the different types of antibiotics used to treat folliculitis and how they are used.
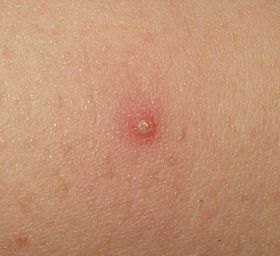
What Is the Best Antibiotic for Folliculitis?
First, in order for your doctor to determine the best antibiotic you need to know what type of infection you have. This is because different pathogens need different treatments. There are also creams and oral antibiotics. These include:
1. Topical Antibiotics for Folliculitis

- Clindamycin (Cleocin)
This comes in a solution that you can place on your skin to treat bacterial infections. It kills staph and strep by keeping the bacteria from growing by blocking certain chemicals they use to stay alive.
Application: Wash and dry your skin thoroughly. Clean skin will allow the medication to work better. Apply the lotion to any affected areas and allow it to dry before putting on clothing.
- Mupirocin (Bactroban)
Mupirocin takes care of bacteria on the skin by stopping it from making proteins that "feed" the bacteria. This causes the bacteria to die off and heals the infection.
Application: Clean your skin, dry it, and apply a very thin film onto the area that is affected. The general directions are to use it three times daily for 10 days or as long as your doctor tells you.
- Erythromycin Cream
This antibiotic cream blocks certain proteins bacteria need to live. The 2 percent cream is effective against most bacterial infections if they are not resistant to this antibiotic.
Application: Wash the affected area and pat dry. Smooth on a thin film of cream over the spots two times daily. Make sure you wash any cream off your hands after application.
- Ketoconazole Cream
Ketoconazole treats fungal infections of the skin. This antibiotic for folliculitis eliminates yeast and fungi that cause folliculitis by breaking open the walls of their cells and exposing them to conditions that inhibit their growth.
Application: In order for antifungal creams to work properly skin needs to be clean and dry. Apply an antifungal cream to the affected area and the area that surrounds the infection. Do not cover or keep moist.
- Gentamicin Cream
Gentamicin cream helps treat folliculitis by halting the growth of bacteria. It is usually more effective in minor cases that have not spread too far or too deep into the follicles.
Application: Clean the affected area with gauze and warm water. Use a clean gauze to pat dry. Apply a small dab of the cream to the area avoiding pressure on the lesions. Cover with a gauze dressing.
2. Oral Antibiotics
- Cephalexin (Keflex)
This cephalosporin is an antibiotic for folliculitis that helps by preventing bacteria from reproducing in your body. It is one of the more commonly used antibiotics for skin infections.
Application: The dose of cephalexin ranges from 250 mg/6 hours to 500 mg/12 hours for a period of 7 to 14 days. If your infection is severe, the doctor may have you take larger doses split up over four times a day.
- Minocycline (Minocin)
This antibiotic is a form of tetracycline that helps treat staph infections. It blocks the proteins that the bacteria need to reproduce and grow in the body thereby stopping the infection.
Application: The usual course of treatment is 200 mg for the first dose, and then 100 mg twice daily for the length of time your doctor thinks is best. If people cannot tolerate these doses, 50 mg can be given 4 times daily.
- Trimethoprim Sulfamethoxazole (Bactrim)
If the folliculitis is caused by MRSA (methicillin resistant Staphylococcus Aureus) then this sulfa medication can be used to fight the infection. It stops the bacteria from growing by not allowing it to use folic acid.
Application: For folliculitis, one tablet is taken twice a day for 10 days or how your doctor tells you to use it.
- Dicloxacillin
Dicloxacillin keeps the cell walls of bacteria from closing up. The bacteria cell walls weaken and break open causing the bacteria to die.
Application: Dicloxacillin is usually 500 mg taken four times a day for one week. If the infection is mild, it is normally only taken for 3 days. Always follow your doctor's instruction to take this medication.
- Ciprofloxacin (Cipro)
Cipro is usually one of the first antibiotic for folliculitis chosen if the infection is drug resistant. It blocks the DNA inside the bacteria so that they cannot reproduce.
Application: Cipro is usually given at doses of 500 to 750 mg two times daily for one to two weeks. People with risk of tendon rupture or connective tissue disease should use caution with this medication.
- Linezolid (Zyvox)
This antibiotic attaches itself to the bacteria and does not allow it to use proteins for growth. It is normally used when folliculitis has been found to be resistant to other antibiotics.
Application: If folliculitis is resistant to other antibiotics, linezolid is used at 600 mg twice daily for 10 to 14 days.
Home Remedies for Folliculitis
If you don't need an antibiotic for folliculitis, you may be able to treat it with over-the-counter remedies to find relief from itching and other discomfort. This may even help prevent a bacterial infection from starting in the first place. Some home treatments include:
1. Antiseptic Wash

These may help to keep bacteria out of the affected area and help prevent infection. Washing with a good soap and plain water can also encourage natural healing of the skin.
How to Apply: Use lukewarm to cool water and wash gently with soap. Rinse well. Pat dry with a soft towel to prevent irritating the skin, do not rub.
2. Chlorine Bleach

This may sound scary, but it's really not. Chlorine bleach that is very diluted has amazing antibacterial properties for the skin. The U.S. military had an outbreak of MRSA out in the field and they found that a bath in dilute chlorine healed the infection. When diluted properly, it is not caustic to the skin.
How to Apply: Make sure you only use 2.2% household bleach. Do not use any stronger. Take ½ cup of bleach and pour into a full bathtub of water. Soak all affected areas for 10 to 15 minutes. Do this only with your body and not your face and head. Rinse yourself with fresh water after soaking and pat yourself dry, do not rub your skin. You can do this 2 times a week.
3. Fragrance-Free Lotion
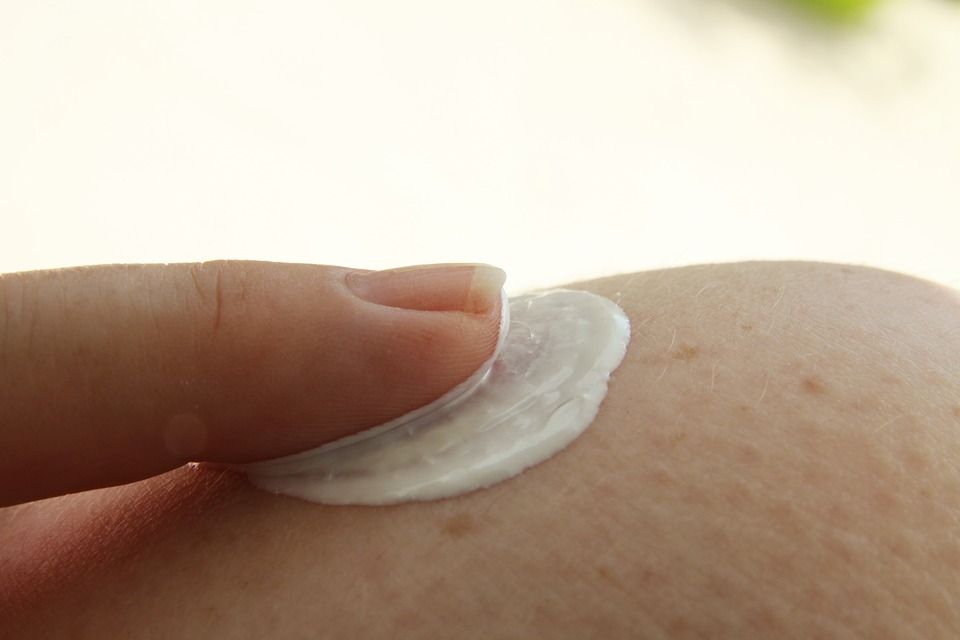
During treatment, use a good quality fragrance-free lotion. Moisture is important when you are healing from folliculitis.
4. Steroid Cream

Another important over-the-counter remedy is steroid cream. This can help relieve the inflammation and pain of folliculitis. Just don't use it over large areas of the body and limit its use to inflamed areas only. Your doctor may recommend you use this with your antibiotic for folliculitis to help control symptoms.
