Some people may discover an abnormal lump on one side of neck. This lump, also called neck mass, may vary in size and shape. Some are very small in size and are almost negligible while others are large and visible to the eyes. Neck lumps can be painless or painful depending on what causes their growth. Most of the lumps are benign or non-cancerous while others are malignantly indicating a more serious medical problem. Diagnosis of the possible causes of is important to properly address the condition and give the best medical treatments. So be sure to see your doctor if you are worried about it.
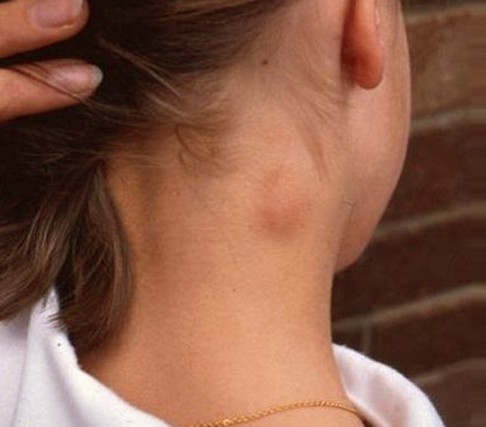
What Causes the Lump on Side of Neck?
1. Enlarged Lymph Nodes
Enlarged lymph nodes are characterized by swelling on the side of the neck or under the jaw. This may indicate a bacterial or viral infection in the area including throat infection, tooth infection, or viral respiratory infection. In most cases, the swollen lymph node in this area are benign. However, it may also suggest cancer in the neck or head.
Tenderness and pain in the lymph nodes, warmth in the affected area, fever, runny nose, sore throat, weight loss, and night sweats may also be experienced.
Treatments:
- To relieve pain and discomfort, take pain relievers.
- For bacterial infections, take antibiotics. However if the infection is due to viruses, let it resolve on its own.
- More serious infection such as HIV needs specific treatment as directed by the experts.
- Immune disorder swelling of the lymph nodes requires treatment at the underlying condition.
- Cancer treatments may involve surgery, chemotherapy, or radiation.
2. Ear Infections
Ear infection, also known as acute otitis media, is a bacterial or viral infection that affects the middle ear. This condition can be painful due to the build-up of fluids that causes the inflammation. It is more common in children than in adults. Frequent or persistent infections can cause more serious hearing problems and complications.
Besides lump on side of neck, patients may experience ear pain, drainage of fluid from the ear, diminished hearing, difficulty in sleeping, irritable, loss of balance, fever, headache, and loss of appetite.
Treatments:
- Take antibiotics, usually in the form of drops, using the proper dosage given by your doctor.
- Use the wait-and-see approach, especially in children, to properly manage the condition.
- Lessen pain by using a warm compress and taking over-the-counter drugs such as acetaminophen and ibuprofen.
- A recurring ear infection may be treated by using ear tubes. This will drain the fluid from the middle ear and help ventilate the area to prevent further accumulation of liquids.
3. Lymphoma
Lymphoma, also known as skin lumps, is a development of fatty tissue underneath the skin. The cause for the appearance of this mass is still unknown, however, hereditary factors may be considered. This may occur in many parts of the body including the shoulders, back, abdomen, thighs, arms, and neck. It is classified as benign tumors, meaning it rarely harmful.
Other symptoms include soft to touch lumps that move easily, paleness, and at times painful.
Treatments:
- Lumps that doesn’t cause any problem or doesn’t affect your movements may be left alone.
- Surgical procedures are a common way to treat largely sized lymphoma. There is also low to no chance of recurring after its removal.
- Liposuction can be done to reduce the size of lymphoma. Since it is fat based, this procedure is really helpful.
- Steroid injections can be used directly to the affected area. This will help shrink the mass but will not totally remove it.
4. Branchial Cleft Cyst
The branchial cleft cyst is a congenital birth abnormality characterized by lumps on one or both sides of the neck. There are several types of branchial cleft defects based on the location of the lumps. The condition is not really dangerous but can cause skin irritation and other conditions.
Besides lump on side of neck, pain, fluid from the neck, and swelling and tenderness of the affected area can also be experienced.
Treatments:
- Take antibiotics to relieve the signs of infection.
- Draining of the fluid from the lump to relieve swelling.
- A surgical procedure to remove the lumps and prevent reoccurrence of the infection.
5. Thyroid Cancer
Thyroid cancer is a common type of endocrine system abnormalities. This is characterized by an abnormal growth of cells in the thyroid gland. People who have a higher risk of developing this disease include women in their 40 years, those with a family history of cancer, and those exposed to radiation.
Other symptoms include pain in the neck that radiates to the ears, the problem in swallowing, breathing troubles, constant wheezing, hoarseness of the voice, and frequent cough.
Treatments:
- A surgical procedure to remove part or all the thyroid gland.
- Chemotherapy
- Radioactive iodine
- External beam radiation therapy
6. Goiter
Goiter is the abnormal enlargement of the thyroid gland. This is primarily due to the lack of iodine in one's diet plan. It may also be due to other factors and diseases such as Grave’s disease, Hashimoto’s disease, cancer, pregnancy, or inflammation. This may be present at birth and occur at any age and any gender.
Besides lump on side of neck, other symptoms like tight feeling in the throat, hoarseness of the voice, coughing, difficulty in breathing, and difficulty in swallowing will also be experienced.
Treatments:
- Small goiters that don’t cause problems can use the wait-and-see approach.
- Medications such as levothyroxine can help slow down the release of hormones causing goiter.
- Aspirin or corticosteroid may be used to treat the inflammation of the thyroid gland.
- Surgical removal of part or all of the thyroid gland.
- Use of radioactive iodine to treat the overactive glands. This can be taken orally to help destroy the thyroid cells that cause a smaller sized lump or goiter.
7. Allergic Reactions
Allergies due to medications may trigger the immune system to react. This may range from mild to severe cases depending on the drugs taken. It is important to be alert at all times on the possible reactions to any drugs and the complications that it may give your body.
Other symptoms include tightening of the throat, difficulty in breathing, abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, dizziness, confusion, and palpitations.
Treatments:
- An antihistamine can be used to relieve the mild symptoms.
- Bronchodilators can be used to reduce coughing and wheezing.
- Corticosteroids can be applied orally or intravenously.
- Epinephrine can be injected for severe cases of allergies.
