Jock itch, or tinea cruris, is a type of fungal infection that affects the skin of the genitals, buttocks, and inner thighs. It causes you to have an itchy, red rash that is often ring-shaped, in the warm and moist areas of the body. Though often bothersome, jock itch is not usually a serious condition. But is it contagious? Find out the answer, and how to control and avoid spreading it.
Is Jock Itch Contagious?
The answer is yes. Jock itch is a contagious fungal skin infection, and it can spread from one person to another in varied ways. The primary method of transmission is by skin-to-skin contact, which is often through sexual activities. This is because fungus likes to grow in moist, warm places in the body and sexual activities provide an ideal environment for it to grow and spread.
Aside from personal contact, another way to transmit jock itch is by sharing clothes, towels, or beddings with someone who is infected with the organisms. One can have a rash that can flake and crack or develop oozing bumps. If you wear someone else’s clothes that contain residual traces of the fungus, you can easily get the disease even without skin contact with another person.
You can also get tinea cruris infection from handling objects that have been used by an infected person. These include chairs and exercise equipment like bicycle seats. People who have athlete’s foot (or tinea pedis) can also get jock itch, so it is always best to wear slippers when using pools and public showers.
How Would I Know If I Got Jock Itch?
Symptoms
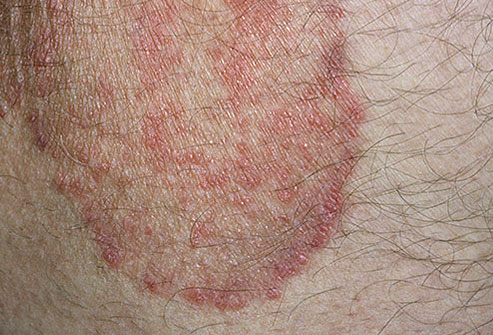
It is easy to diagnose jock itch just by looking at the location and appearance of the rash. It usually begins with mild itching in your groin, which gets worse and sometimes unbearable when you are in a warm and humid environment. The rash usually affects both sides, especially on the skin folds.
- The jock itch rash may become rough, dry, and bumpy. It can develop bumps with pus and then start oozing. Sometimes, the itchy, red rash spreads to the thighs and genitals, including your labia, vagina, or scrotum, and penis, as well as the anus.
- Women may develop white vaginal discharge and yeast infection with jock itch infections. Men who are not circumcised may develop infection on the head of their penis.
- In severe infections, you may be very uncomfortable. You can also develop complications such as skin breaks, ulcers, open sores, and cellulitis (rare).
Is jock itch contagious? Definitely, so if you have these symptoms, go to your doctor for professional diagnosis and treatment.
Test
If the diagnosis is not clear, your doctor may need to take skin scrapings to get samples from infected areas. These are then send to the lab and viewed under a microscope. The fungus may also be grown in the lab for proper identification and treatment, which is called a culture.
How Is Jock Itch Treated?
Know that you are aware of the answer to the question “Is jock itch contagious?” you might be wondering about how to deal with this condition. There are many over-the-counter products available to treat jock itch and they come in different forms, including creams, powders, and sprays. Sometimes, you may need a doctor’s prescription for antifungal cream or medication if these products don’t work as a relief to your symptoms.
In treating a fungal infection, it is important to always keep the affected areas clean and dry. Here are some tips in treating jock itch:
- Wash the skin, then dry the area with a clean towel. Use another clean towel to dry the rest of your body to prevent the infection from spreading to other areas.
- Apply antifungal cream/powder/spray as directed. Be sure to continue treatment for the whole amount of time recommended even if your symptoms improve immediately to prevent recurrence of the infection.
- Change clothes, including your underwear and socks every day.
- Treat other fungal infections like athlete's foot.
Visit your doctor if your symptoms do not improve after 2 weeks or worsen. The doctor may prescribe stronger antifungal medications to control the infection. These include:
- Topical antifungal medications like econazole or oxiconazole
- Oral antifungal medications like fluconazole, itraconazole, or terbinafine
Oral medications may have unpleasant side effects such as headache, upset stomach, or decreased liver function. If you get any of these side effects, call your doctor. It is also important to tell your doctor if you are taking other medications or supplements that may interact with your antifungal medications.
Preventing Jock Itch
Because the answer to “Is jock itch contagious?” is positive, you’d better avoid having them in the first place. To prevent jock itch or its recurrence, here are some helpful tips:
- Wash workout clothes after every use.
- Do not store damp clothes and towels in lockers or duffel bags.
- Change your socks and underwear daily, or more often if you engage in heavy activities that make you sweat.
- If you are susceptible to sweating and jock itch, use antifungal drying powders after bath.
- Wear loose-fitting clothes, especially from your waist down.
- If you have athlete's foot, wear socks before putting on your underwear so the fungi from the feet do not make their way to your groin.
